Creating Backups to Remote Storage Systems Using REC and QuickOPC
This section describes the operation of periodically backing up the business volume on the remote storage systems using REC in asynchronous stack mode and QuickOPC. Even if a storage system with an operation volume is damaged due to a disaster, data can be guaranteed at the time of backup. Even if the line bandwidth of the copy path is smaller than that of creating the mirrored volume in the remote storage system, backups can be created in the remote storage system while minimizing the loss of responsiveness of the business volume.
When using the REC function in asynchronous stack mode, it is assumed that the backup is updated once a day or so (RPO > 1 Day). Compared to creating a mirrored volume, the copy path requires less line bandwidth but RPO is longer (For Synchronous mode, RPO = 0; for Asynchronous Consistency mode, RPO = between few seconds to few minutes).
If the line bandwidth of the copy path is sufficient and you want a shorter RPO, consider using the REC feature in synchronous or asynchronous consistency mode.
In the case of operation in the asynchronous stack mode, since the order guarantee of the data written in the business volume is not performed when the data is transferred, the data in the backup volume of the remote storage system cannot be referenced during the data transfer. Therefore, it is necessary to create a Clone of the backup volume on the remote storage system before data transfer starts so that data can be recovered from the Clone on the remote storage system even if the local storage system is damaged due to a disaster during data transfer.
Operation Overview
The following is an overview of operations using the REC in asynchronous stack mode and QuickOPC functions to back up business volumes in a remote storage system.
Before the start of operation
The backup volume of the remote storage system matches the data of the Clone.
Figure: State of Data before the Start of Operation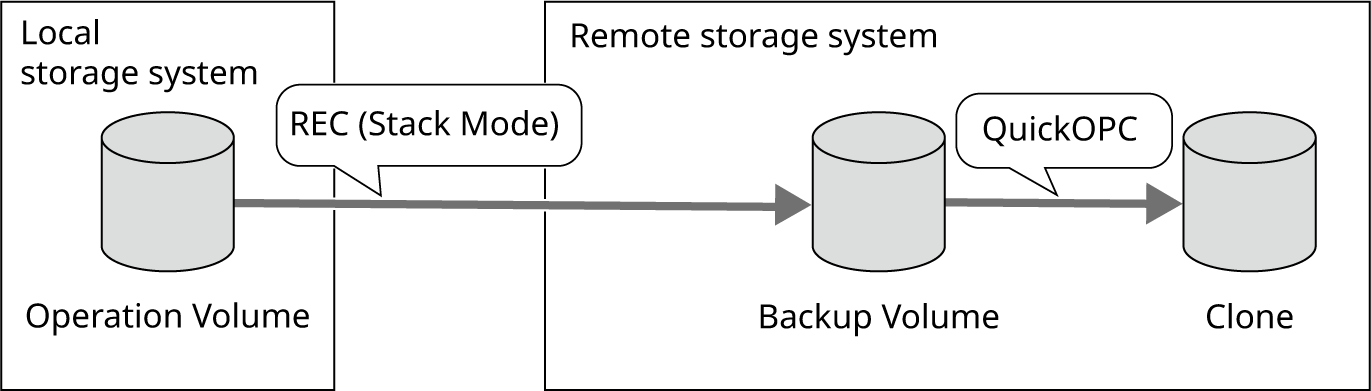
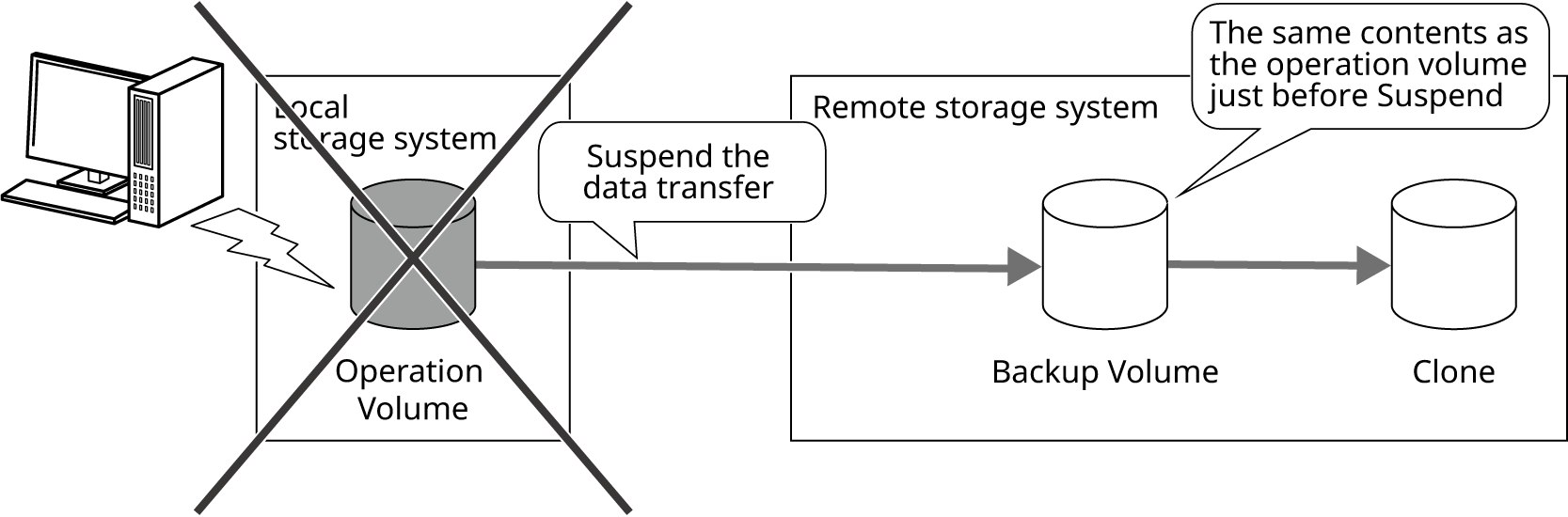
During an operation
Suspend the REC Session immediately before starting an operation to prevent data transfer.
The data of the operation volume is updated.
The data in the operation volume and the backup volume on the remote storage system do not match.
If the local storage system is damaged due to a disaster, data can be recovered from the backup volume in the remote storage system.
Figure: Status of Data during an Operation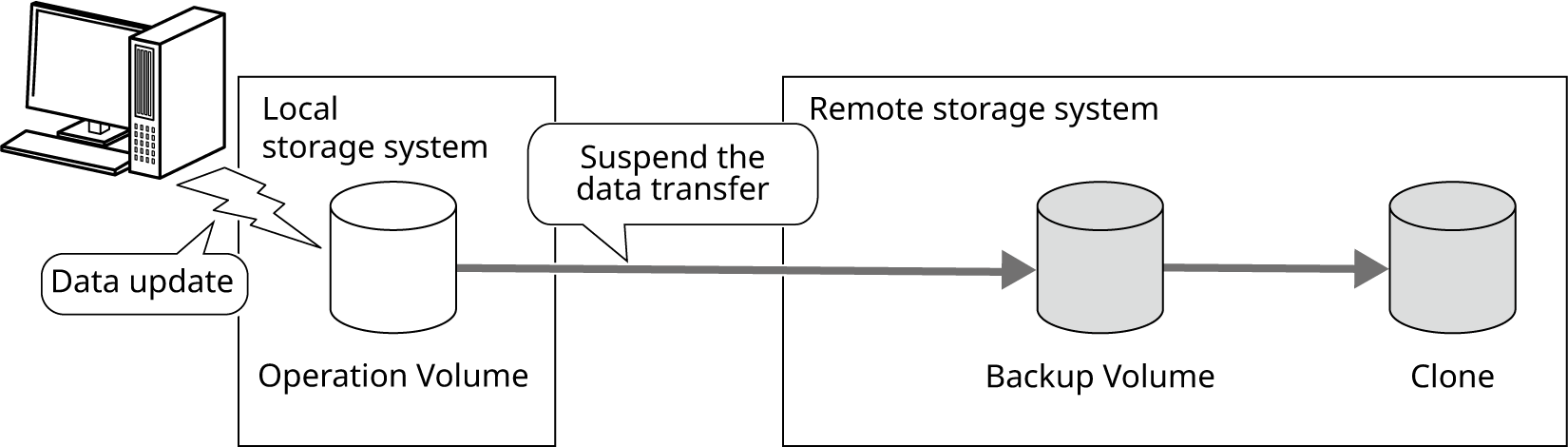
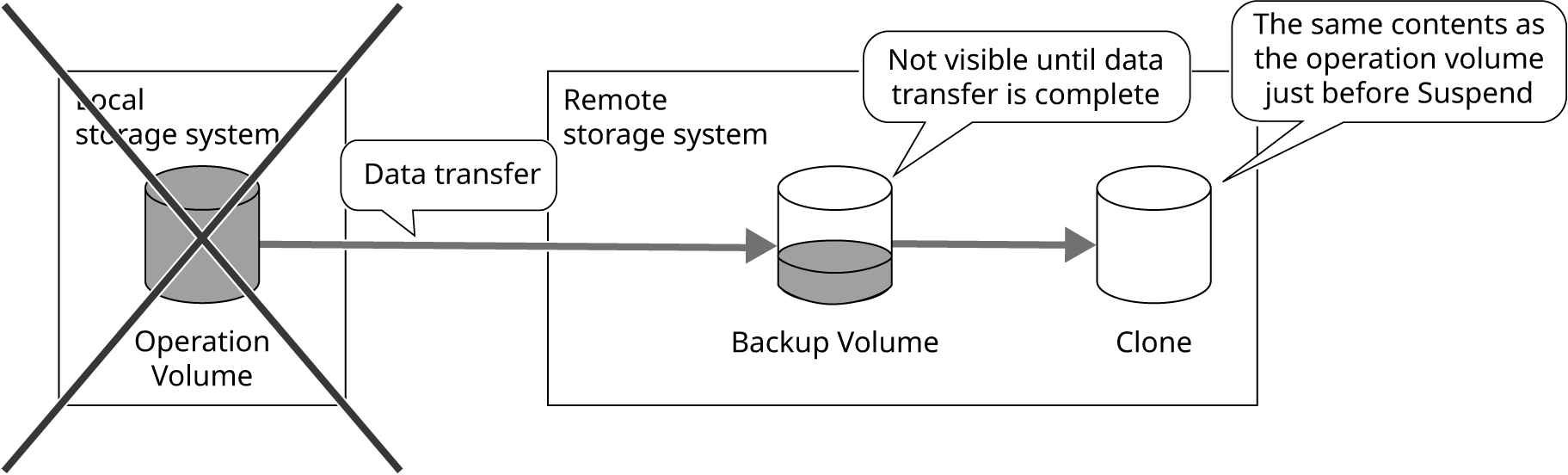
After the operation is completed
Resume the REC Session and transfer the operation volume data to the remote storage system.
Since data transfer does not guarantee order, the backup volume of the remote storage system is not visible during data transfer.
If the local storage system is damaged due to a disaster, data can be recovered from the Clone of the backup volume in the remote storage system.
Figure: Status of Data after the Operation is Completed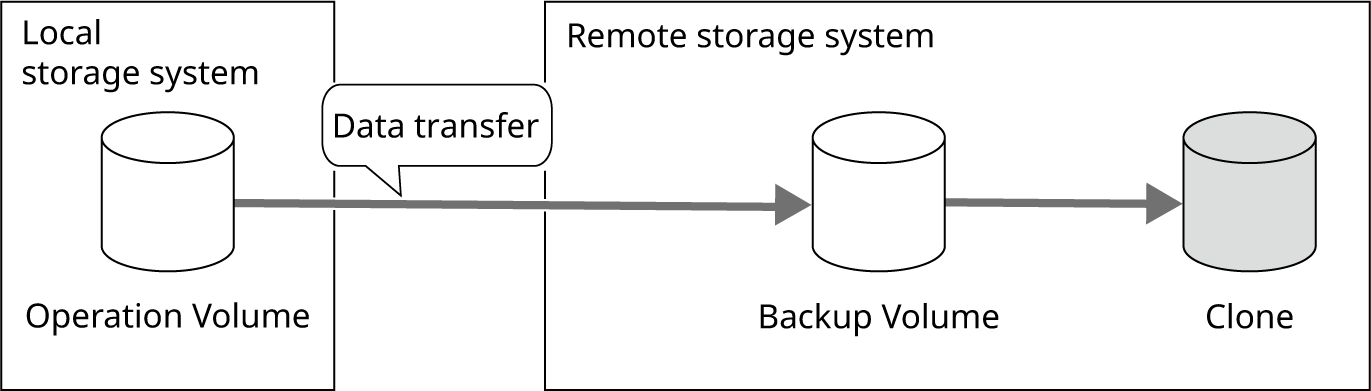
During an operation (second time and later)
Suspend the REC Session immediately before starting an operation to prevent data transfer during the operation.
Just before the start of the operation, it is necessary to make all the update data during the last operation transferred (keep the data of the operation volume and the backup volume of the remote storage system consistent).
Resynchronize the Clone of the backup volume in the remote storage system to make the backup volume in the remote storage system and Clone data identical.
If the local storage system is damaged due to a disaster during operations, the data just before the start of operations can be recovered from the data in the backup volume of the remote storage system.
Figure: Status of the Data during an Operation (Second Time and Later)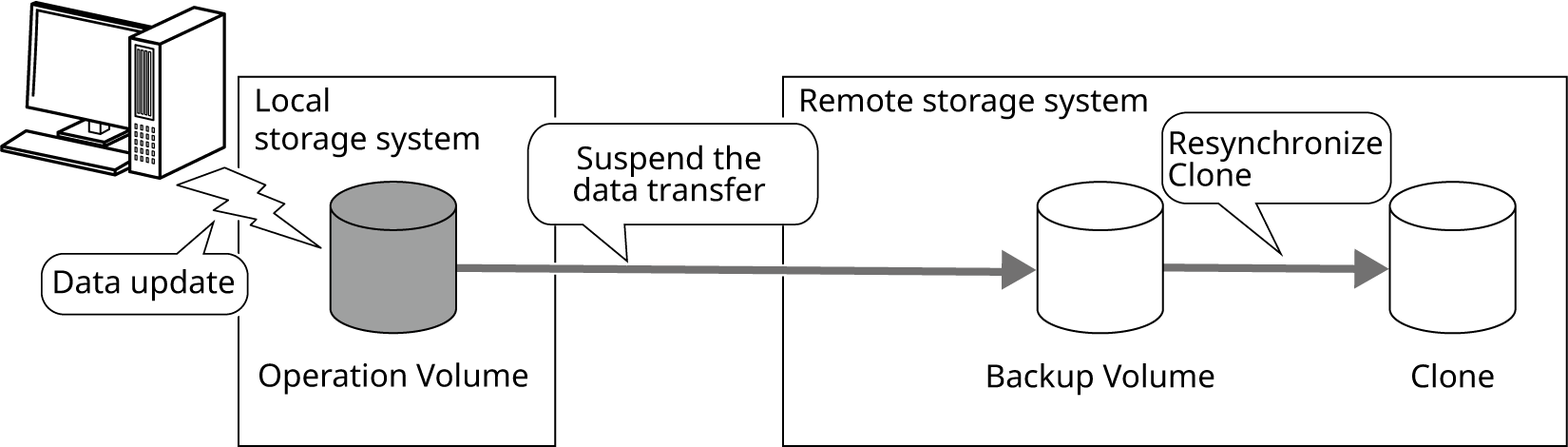
After the operation is completed (second time and later)
If the local storage system is damaged due to a disaster during data transfer, the data from the previous end of operation can be recovered from the Clone of the backup volume of the remote storage system.
Figure: Status of the Data after the Operation Is Completed (Second Time and Later)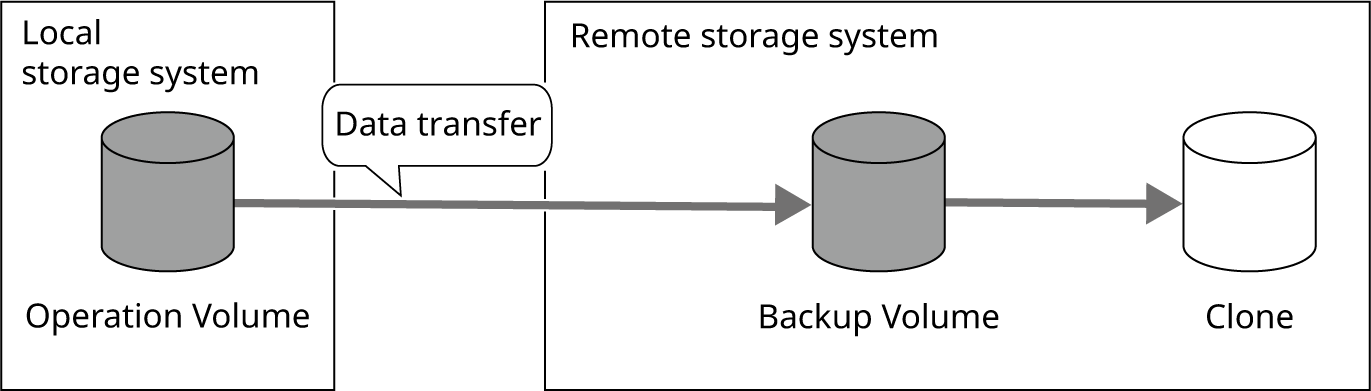
Operation Overview (On Restore)
This section describes an overview to recover data from a backup volume or Clone of a remote storage system in an environment where operation volume backups are regularly created on the remote storage system using the REC function in asynchronous stack mode and QuickOPC.
Depending on when the local storage system was damaged due to a disaster, the restoration is performed from the backup volume of the remote storage system or from the Clone of the backup volume of the remote storage system.
If the operation volume is damaged due to a disaster during Suspend of the REC Session, recover the data from the backup volume in the remote storage system. The data of the operation volume can be recovered to just before the suspension, but the data that is updated after the suspension cannot be recovered.
If the REC Session is in the process of transferring data, the data will be recovered from the Clone of the backup volume in the remote storage system.
Since the order of data transfer is not guaranteed, data in the backup volume of the remote storage system cannot be referenced during data transfer. Therefore, data must be recovered from the Clone of the backup volume in the remote storage system that was resynchronized during Suspend.
When the data is recovered from a Clone, the data of the operation volume just before the suspension can be recovered, but the data that is updated after the suspension cannot be recovered.
RESTful API and Sample Scripts for Operation Use
Preparation
Create a Clone of the backup volume (destination volume for REC in Asynchronous Stack Mode) and the backup volume on the remote storage system. Use rec_stack_create.py.
Operation
Before beginning operation (before updating the operation volume), suspend the REC Session and create a backup of the operation volume in the remote storage system. At the same time, it starts resynchronizing the Clone of the backup volume, and copies the data transferred before the start of operation to the Clone. Use rec_stack_before_operation.py.
At the end of the operation (after updating the operation volume), resume the REC Session and transfer the updated data of the operation volume to the remote storage system. Use rec_stack_after_operation.py.
Restore
If the REC Session is Suspended, reverse the REC Session to restore the data from the backup volume in the remote storage system.
If the REC Session is not Suspended, restore the data from the Clone of the backup volume by inverting the REC Session and creating a Restore OPC Session from the Clone to the backup volume. Use rec_stack_recover.py.
Deletion
To delete a Clone of the backup volume, use DELETE /volume/{volume_id} API. For more information, see the description of Deleting Volumes.
To delete a backup volume, force delete the REC Session, and then delete the destination Volume. For forced deletion of the Copy Session, use DELETE /copysession/{copysession_id} API. For deletion of volumes, use DELETE /volume API. For more information, see the description of Deleting a Copy Session or Deleting Multiple Volumes.
If only the REC Session is deleted and the backup volume is still being utilized in the remote storage system, the REC Session should be deleted by using copysession_delete.py or DELETE /copysession/{copysession_id} API.
Notes
Suspend will fail if there is any untransferred data when suspending the REC Session. Perform Suspend with no untransferred data remaining.
If Suspend is required to change the transfer mode, execute Suspend with force specification.
If data transfer to the remote storage system is resumed while data is being copied to the Clone of the backup volume of the remote storage system, recovery using the data in the remote storage system will not be possible until data is copied to the Clone.
Before transferring data from the remote storage system, make sure that data has been copied to the Clone.
For notes on cloning a remote storage system backup volume, see Creating Regular Full Backups with QuickOPC.



