Eco-mode
Eco-mode is a function that reduces power consumption for limited access disks by stopping the disks rotation during specified periods or by powering off the disks.
Disk spin-up and spin-down schedules can be set for each RAID group or TPP. These schedules can also be set to allow backup operations.

The Eco-mode function of the ETERNUS DX is specialized for reducing power consumption attributed to Massive Arrays of Idle Disks (MAID). The operational state for stopping a disk can be selected from two modes: "stop motor" or "turn off drive power".
The disks to be controlled are SAS disks and Nearline SAS disks.
Eco-mode cannot be used for the following drives:
Global Hot Spares (Dedicated Hot Spares are possible)
SSDs (NVMe SSDs and SAS SSDs)
SSD SEDs (NVMe SSD SEDs and SAS SSD SEDs)
The Eco-mode schedule cannot be specified for the following RAID groups or pools:
No volumes are registered
Configured with SSDs (NVMe SSDs and SAS SSDs)
Configured with SSD SEDs (NVMe SSD SEDs and SAS SSD SEDs)
RAID groups to which the volume with Storage Migration path belongs
RAID groups that are registered as an REC Disk Buffer
RAID groups that are registered as Extreme Cache Pools
TPPs where the Deduplication function, the Compression function, or both are enabled
FTSP
For RAID groups with the following conditions, the Eco-mode schedule can be set but the disks motor cannot be stopped or the power supply cannot be turned off:
SDPVs are registered
ODX Buffer volumes are registered
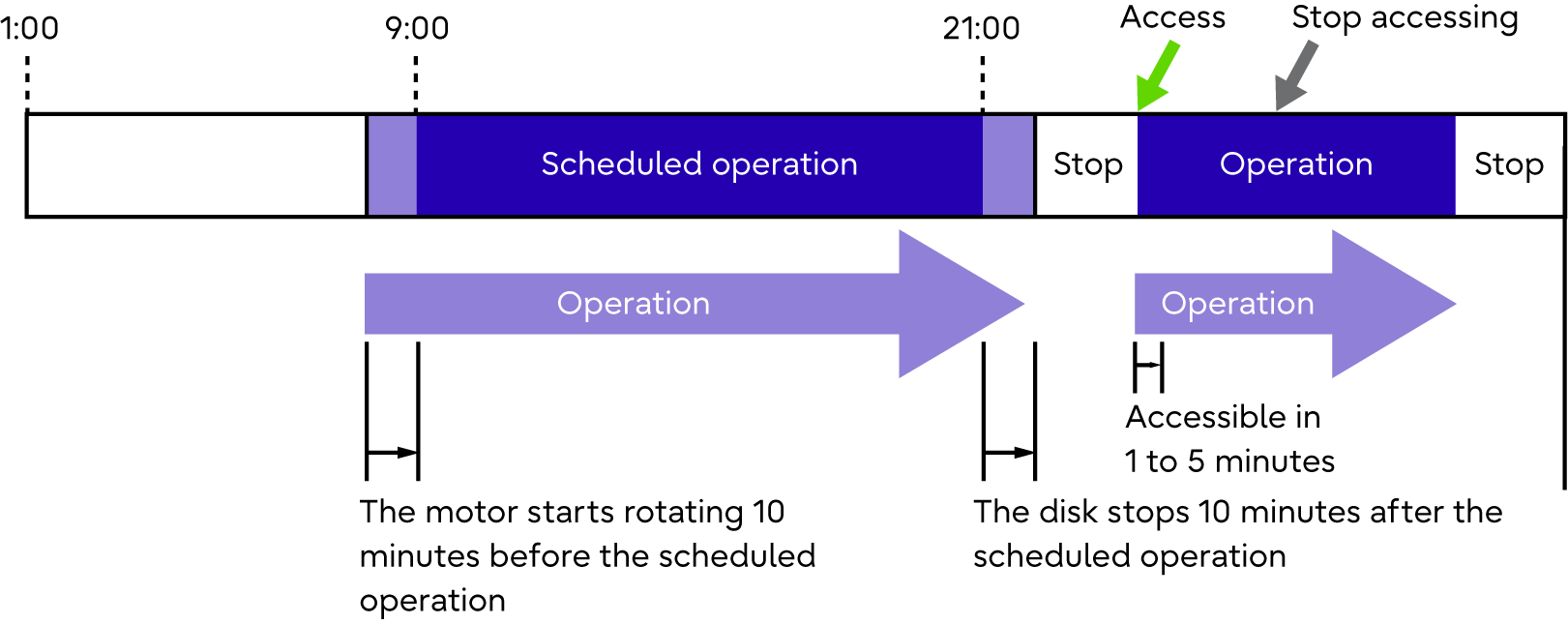
If disk access occurs while the disk motor is stopped, the disk is immediately spun up and can be accessed within one to five minutes.
The Eco-mode function can be used with the following methods:
Schedule control
Controls the disk motors by configuring the Eco-mode schedule on ETERNUS Web GUI or ETERNUS CLI. The operation time schedule settings/management is performed for each RAID group and TPP.
External application control (software interaction control)
Disk motor is controlled for each RAID group on ETERNUS SF Software.
The disk motors are controlled by interacting with applications installed on the server side and responding to instructions from the applications. Applications which can be interacted with are as follows:
ETERNUS SF Storage Cruiser
ETERNUS SF AdvancedCopy Manager
The hierarchical storage management software can be also linked with the Eco-mode function.
When using the Eco-mode function with the hierarchical storage management software, an Eco-mode disk operating schedule does not need to be set. A drive in a stopped condition starts running when it is accessed.
The following table shows the specifications of Eco-mode.
Item |
Description |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|
Number of registrable schedules |
64 |
Up to 8 events (during disk operation) can be set for each schedule. |
Host I/O monitoring interval (*1) |
30 minutes (default) |
Monitoring time can be set from 10 to 60 minutes. This setting can only be changed by users with the Maintenance Operation policy. |
Disk motor spin-down limit count (per day) |
25 (default) |
The number of times the disk is stopped can be set from 1 to 25. When it exceeds the upper limit, Eco-mode becomes unavailable, and the disks keep running. This setting can only be changed by users with the Maintenance Operation policy. |
Target drive |
SAS disks (*2) Nearline SAS disks (*2) |
SSDs and SSD SEDs are not supported. |
| *1 | : | The monitoring time period to check if there is no access to a disk for a given length of time and stop the drive. |
| *2 | : | Self Encrypting Drives (SEDs) are also included. |
To set Eco-mode schedules, use ETERNUS Web GUI, ETERNUS CLI, ETERNUS SF Storage Cruiser, or ETERNUS SF AdvancedCopy Manager. Note that schedules that are created by ETERNUS Web GUI or ETERNUS CLI and schedules that are created by ETERNUS SF Storage Cruiser or ETERNUS SF AdvancedCopy Manager cannot be shared. Make sure to use only one type of software to manage a RAID group.
Use ETERNUS Web GUI or ETERNUS CLI to set Eco-mode for TPPs. ETERNUS SF Storage Cruiser or ETERNUS SF AdvancedCopy Manager cannot be used to set the Eco-mode for TPPs and FTRPs.
Specify the same Eco-mode schedule for the RAID groups that configure a WSV. If different Eco-mode schedules are specified, activation of stopped disks when host access is performed occurs and the response time may increase.
Eco-mode schedules are executed according to the date and time that are set in the ETERNUS DX. To turn the disk motor on and off according to the specified schedule, set the Network Time Protocol (NTP) server in the date and time setting in ETERNUS Web GUI to automatically adjust the date and time.
If the number of disks that are activated in a single drive enclosure is increased, the time for disk activation may take longer (about 1 to 5 minutes). This is because all of the disks cannot be activated at the same time.
Even if the disk motor is stopped and spun up repeatedly according to the Eco-mode schedule, the failure rate is not affected compared to when the motor is always on.
Even if Eco-mode is enabled, the disk motor may not stop or the disk may not turn off in an environment where the server OS or software regularly accesses the ETERNUS DX.
The operation time of disks varies depending on the Eco-mode schedule and the disk access.
Access to a stopped disk outside of the scheduled operation time period causes the motor of the stopped disk to be spun up, allowing normal access in about one to five minutes. When a set time elapses since the last access to a disk, the motor of the disk is stopped.
If a disk is activated from the stopped state more than a set amount of times in a day, the Eco-mode schedule is not applied and disk motors are not stopped by the Eco-mode.
(Example 1) Setting the Eco-mode schedule via ETERNUS Web GUI
Operation schedule is set as 9:00 to 21:00 and there are no accesses outside of the scheduled period
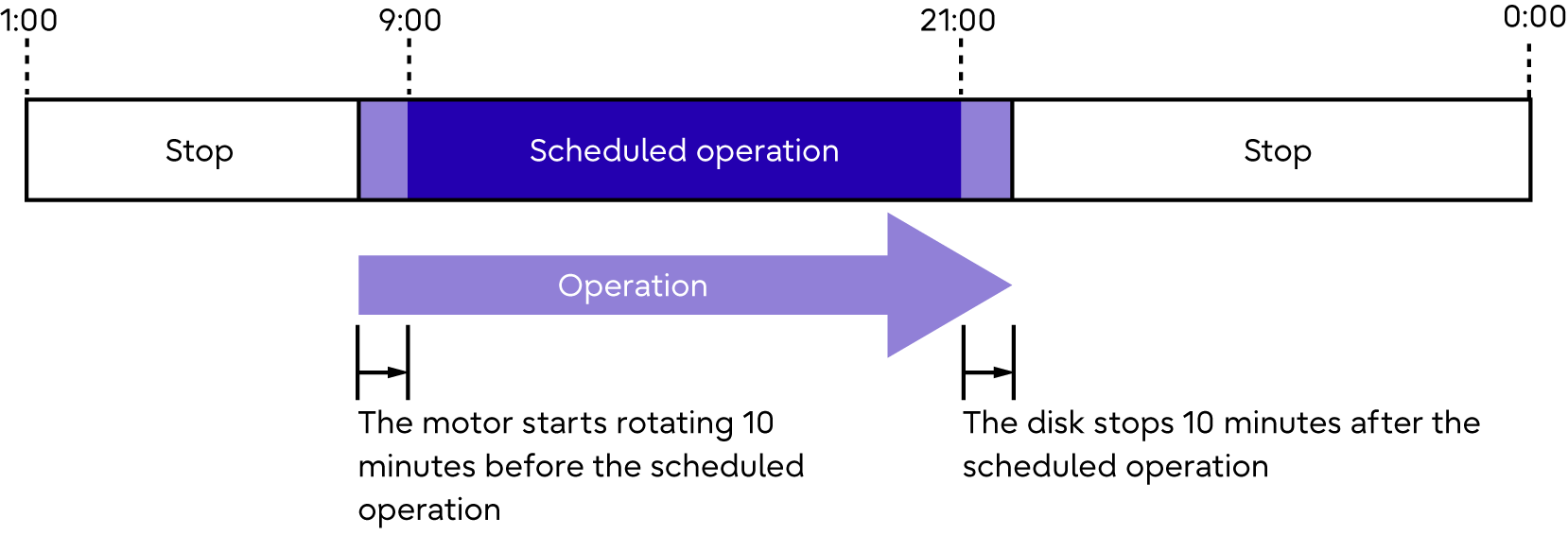
(Example 2) Setting the Eco-mode schedule via ETERNUS Web GUI
Operation schedule is set as 9:00 to 21:00 and there are accesses outside of the scheduled period