Multitenancy
Multitenancy is a function that divides the management of resources on a per tenant basis so that one storage system can be shared by multiple organizations. Costs can be reduced compared to a single tenant with a dedicated storage, and the maintenance load can be reduced by consolidating the storage.
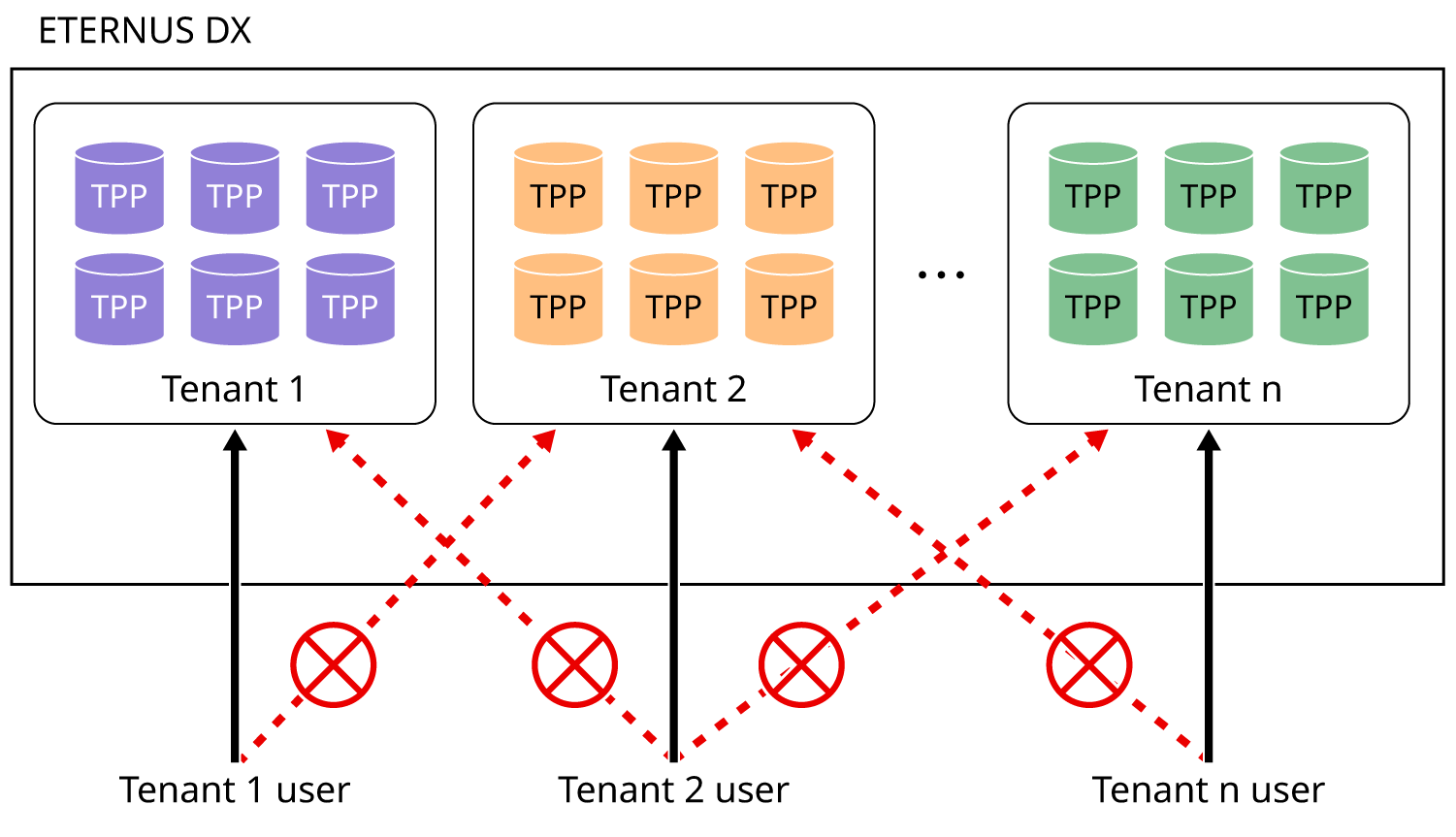
In a Multitenancy system, tenant information can be added to resources such as volumes, TPPs, and hosts.
In addition, tenant information can be added to user accounts. User accounts with tenant information are called "tenant users". Multitenancy operates by limiting the following for tenant users.
The resources created by a tenant user are resources that all belong to the tenant of that user.
Resources that belong to the tenant of that user cannot be referenced from users of other tenants. This prevents resource information leakage.
Resources that belong to the tenant of that user cannot be operated by users of other tenants. This deters incorrect operations that affect production.
The following functions are not supported for tenant users.
ETERNUS Web GUI (Normal View)
ETERNUS Web GUI (Easy Administration View) is available.
ETERNUS CLI
Assigning roles other than "Monitor" or "StorageAdmin"
The tenants created by Multitenancy are described below.
The maximum number of tenants that can be created in one storage system is 32.
A tenant ID (0 to 31) and tenant name can be set for each tenant.
The resources that can be assigned to tenants are TPPs, volumes (TPVs), and hosts (WWNs, iSCSI Hosts). Physical resources (such as drives and CA ports) cannot be assigned.
There is no limit for each tenant for resources that are assigned to tenants. A resource can be assigned to a tenant if the total number of resources in all the tenants and common resources is within the maximum value of the storage system.



