Automated Storage Tiering
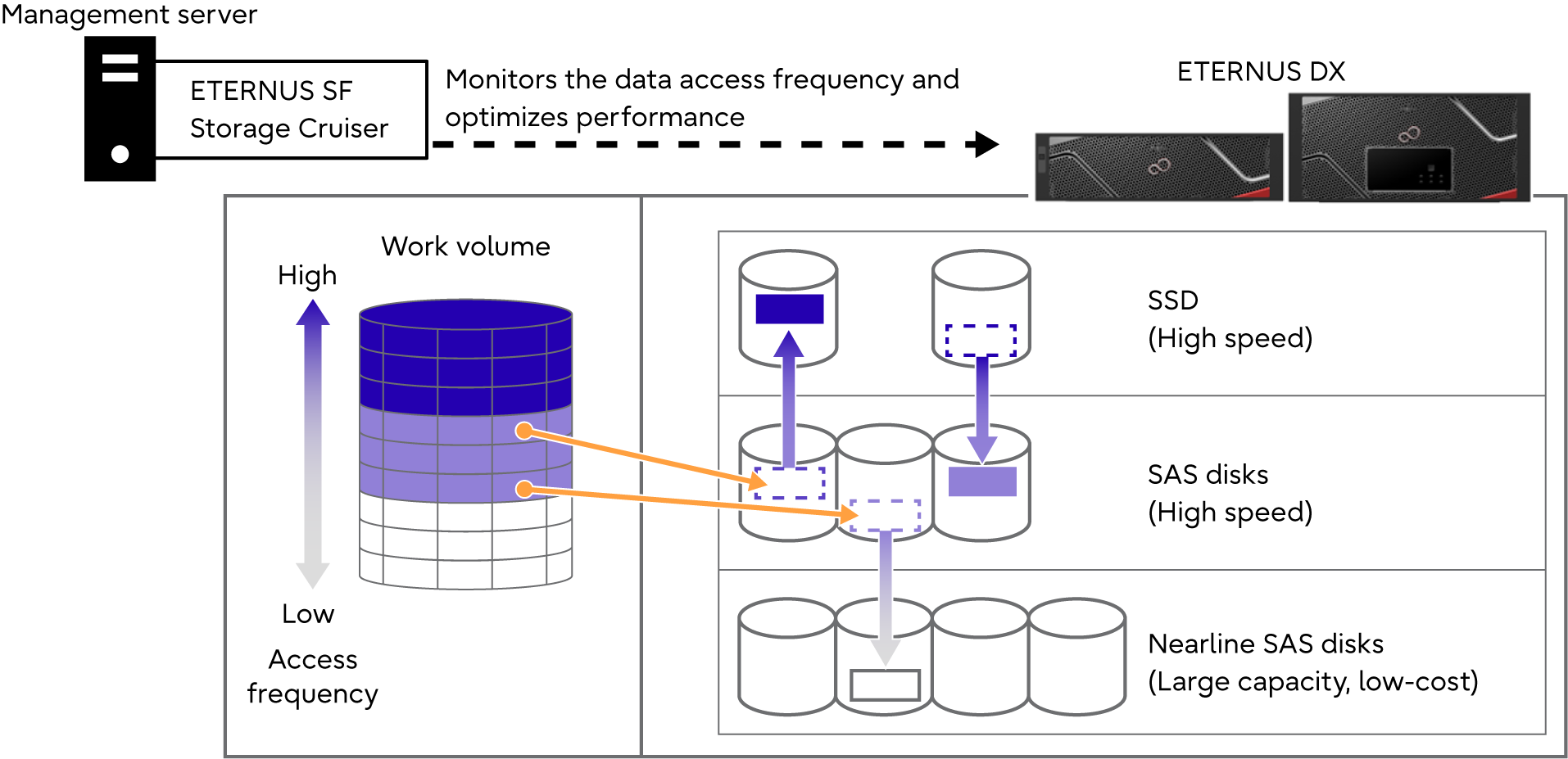
The ETERNUS DX uses the Automated Storage Tiering function of ETERNUS SF Storage Cruiser to automatically change data allocation during operations according to any change in status that occurs. ETERNUS SF Storage Cruiser monitors performance and determines the redistribution of data based on this performance data. The ETERNUS DX uses the Flexible Tier function to move data in the ETERNUS DX according to requests from ETERNUS SF Storage Cruiser.
The Flexible Tier function automatically redistributes data in the ETERNUS DX according to access frequency in order to optimize performance and reduce operation cost. Storage tiering (SSDs, SAS disks, Nearline SAS disks) is performed by moving frequently accessed data to high speed drives such as SSDs and less frequently accessed data to cost effective disks with large capacities. Data can be moved in blocks (252MB) that are smaller than the volume capacity.
The data transfer unit differs depending on the chunk size. The following table shows the relationship between the data transfer unit and the chunk size.
Chunk size |
Transfer unit |
|---|---|
21MB |
252MB |
42MB |
504MB |
84MB |
1,008MB |
168MB |
2,016MB |
336MB |
4,032MB |
672MB |
8,064MB |
1,344MB |
16,128MB |
With the Automated Storage Tiering function, Nearline SAS disks can be used to reduce installation costs and retain performance.
Furthermore, because data is reallocated automatically, it can reduce the workload on the administrator for designing storage performance.
Flexible Tier uses pools configured with multiple RAID groups (Flexible Tier Sub Pools: FTSP) and larger pools (Flexible Tier Pools: FTRP) comprised of FTSP layers. Volumes used by Flexible Tier are referred to as Flexible Tier Volumes (FTV).
Settings and operation management for the Flexible Tier function are performed with ETERNUS SF Storage Cruiser. For more details, refer to "ETERNUS SF Storage Cruiser Operation Guide for Optimization Option".
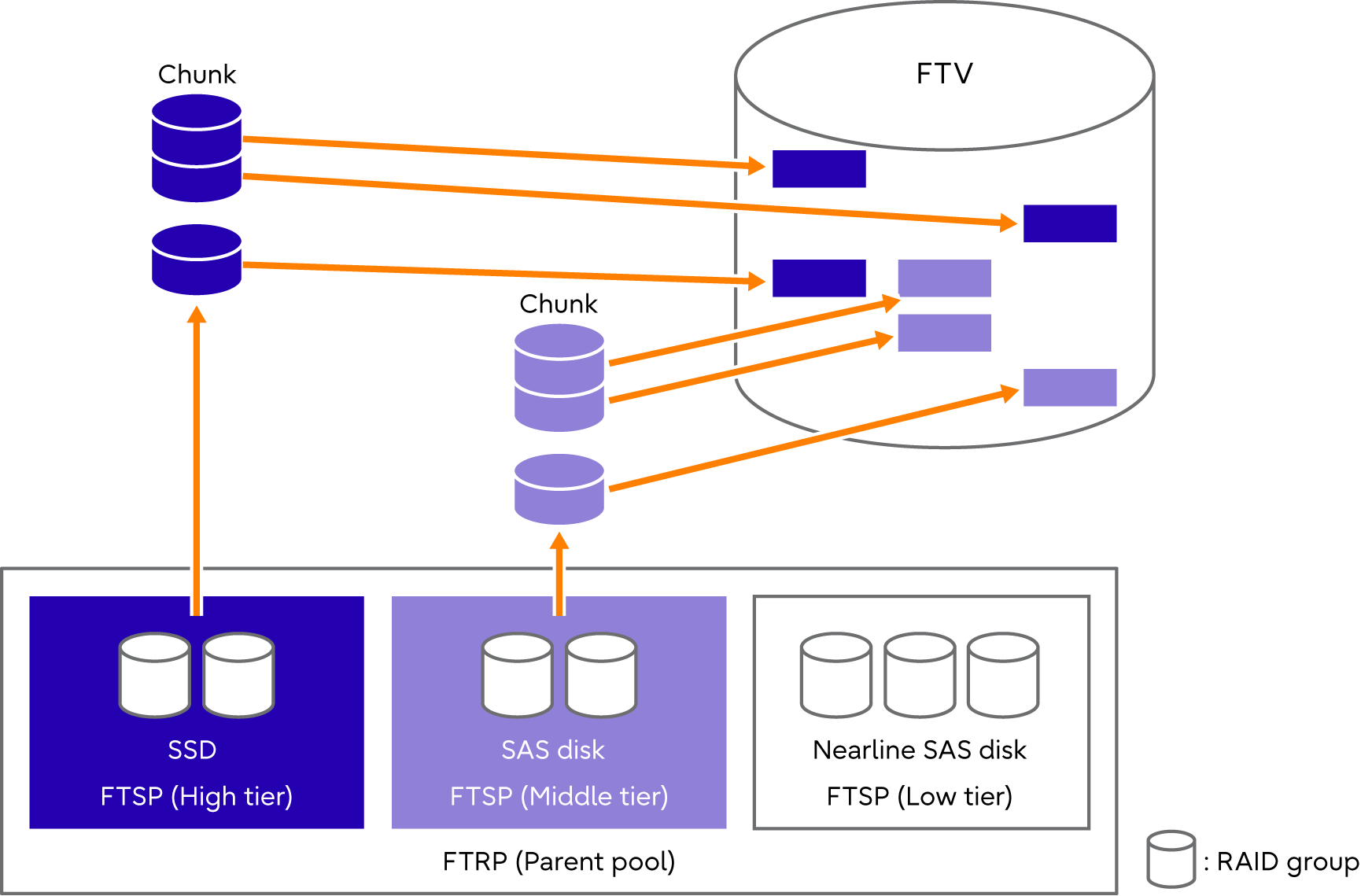
Flexible Tier Pool (FTRP)
An FTRP is a management unit for FTSP to be layered. Up to three FTSPs can be registered in one FTRP. This means that the maximum number of layers is three.
The priority orders can be set per FTSP within one FTRP. Frequently accessed data is stored in an FTSP with a higher priority. Because FTSPs share resources with TPPs, the maximum number of FTSPs which can be created is decreased when TPPs are created.
For data encryption, specify encryption for a pool when creating an FTRP or create an FTSP with a Self Encrypting Drive (SED).
Flexible Tier Sub Pool (FTSP)
An FTSP consists of one or more RAID groups. The FTSP capacity is expanded in units of RAID groups. Add RAID groups with the same specifications (RAID level, drive type, and number of member drives) as those of the existing RAID groups.
The following table shows the maximum number and the maximum capacity of FTSPs that can be registered in an ETERNUS DX.
Table: The Maximum Number and the Maximum Capacity of FTSPs Item
ETERNUS DX600 S6
ETERNUS DX900 S6
ETERNUS DX8900 S6
Maximum number of Flexible Tier Pools
64
64
Maximum number of Flexible Tier Sub Pools (*1)
256
256
Maximum capacity of the Flexible Tier Sub Pools (*2)
98,304TB
(96PB)
524,288TB
(512PB)
Total capacity of the Flexible Tier Volumes (*3)
98,304TB
(96PB)
524,288TB
(512PB)
*1 : The maximum total number of Thin Provisioning Pools and FTSPs.
*2 : The maximum pool capacity is the capacity that combines the FTSP capacity and the Thin Provisioning Pool capacity in the ETERNUS DX. The maximum pool capacity of an FTRP is the same as the maximum pool capacity of a Flexible Tier Sub Pool.
*3 : Same as the maximum capacity of the Flexible Tier Sub Pools. The actual maximum capacity varies depending on the physical capacity that is configurable in the ETERNUS DX.
NoteThe ETERNUS DX8900 S6 has a total usage capacity limit for FTRPs in which Flexible Tier evaluations can be performed concurrently. For details, refer to the manual for ETERNUS SF Storage Cruiser.
The RAID levels and the configurations, which can be registered in the FTSP, are the same as those of a TPP. The following table shows the RAID configurations that can be registered in an FTSP.
Table: Levels and Configurations for a RAID Group That Can Be Registered in an FTSP RAID level
Number of configurable drives
Recommended configurations
RAID0
4 (4D)
—
RAID1
2 (1D+1M)
2 (1D+1M)
RAID1+0
4 (2D+2M), 8 (4D+4M), 16 (8D+8M), 24 (12D+12M)
8 (4D+4M)
RAID5
4 (3D+1P), 5 (4D+1P), 7 (6D+1P), 8 (7D+1P), 9 (8D+1P), 13 (12D+1P)
4 (3D+1P), 8 (7D+1P)
RAID6
6 (4D+2P), 8 (6D+2P), 9 (7D+2P), 10 (8D+2P)
8 (6D+2P)
RAID6-FR
13 ((4D+2P) × 2 + 1HS), 17 ((6D+2P) × 2 + 1HS),
31 ((8D+2P) × 3 + 1HS), 31 ((4D+2P) × 5 + 1HS)
17 ((6D+2P) × 2 + 1HS)
Flexible Tier Volume (FTV)
An FTV is a management unit of volumes to be layered. The maximum capacity of an FTV is 128TB. Note that the total capacity of FTVs must be less than the maximum capacity of FTSPs.
When creating an FTV, the Allocation method can be selected.
Thin
When data is written from the host to an FTV, the physical area is allocated to a created virtual volume. The physical storage capacity can be reduced by allocating a virtualized storage capacity.
Thick
When creating a volume, the physical area is allocated to the entire volume area. This can be used for volumes in the system area to prevent a system stoppage due to a pool capacity shortage during operations.
In general, selecting "Thin" is recommended. The Allocation method can be changed after an FTV is created.
Perform a TPV/FTV capacity optimization if "Thick" has changed to "Thin". By optimizing the capacity, the area that was allocated to an FTV is released and the FTV becomes usable. If a TPV/FTV capacity optimization is not performed, the usage of the FTV does not change even after the Allocation method is changed.
The capacity of an FTV can be expanded after it is created.
For details on the number of FTVs that can be created, refer to Volume.
Threshold Monitoring of Used Capacity
When the used capacity of an FTRP or an FTV reaches the threshold, an alarm notification can be sent from ETERNUS SF Storage Cruiser. There are two types of thresholds: "Attention" and "Warning". A different value can be specified for each threshold type.
Make sure to add drives before free space in the FTRP runs out, and add FTSP capacity from ETERNUS SF Storage Cruiser.
FTRP Thresholds
There are two FTRP usage thresholds: Attention and Warning.
Table: FTRP Thresholds Threshold
Selectable range
Default
Setting conditions
Attention
5 (%) – 80 (%)
75 (%)
Attention threshold £ Warning threshold
The "Attention" threshold can be omitted.
Warning
5 (%) – 99 (%)
90 (%)
FTV Thresholds
There is only one FTV usage threshold: Attention. If there is insufficient capacity for the FTV unallocated space in the pool free space, an alarm notification is sent. The threshold is determined by the ratio of free space in the FTSP and the unallocated FTV capacity.
Table: FTV Thresholds Threshold
Selectable range
Default
Attention
1 (%) – 100 (%)
80 (%)
When the Flexible Tier function is enabled, 64 work volumes (physical capacity is 0MB) are created. The maximum number of volumes that can be created in the ETERNUS DX decreases by the number of work volumes that are created.
If an FTSP or an FTRP includes one or more RAID groups that are configured with Advanced Format drives, the write performance may be reduced when accessing FTVs created in the relevant FTSP or FTRP from an OS or an application that does not support Advanced Format.
The FTRP capacity that can be used for VVOLs differs from the maximum Thin Provisioning Pool capacity. For details, refer to VMware VVOL.



