Volume
This section explains volumes.
Logical drive areas in RAID groups are called volumes.
A volume is the basic RAID unit that can be recognized by the server.
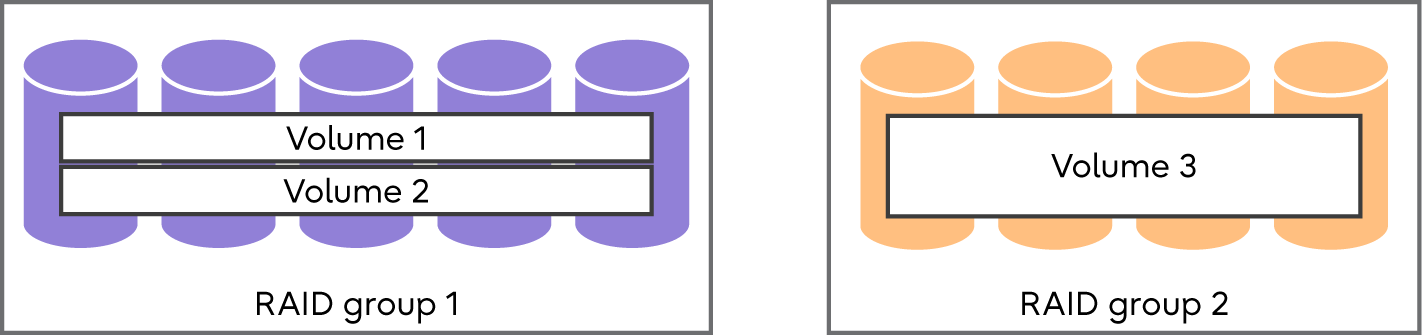
The maximum capacity of a volume is 128TB. However, the maximum capacity of volume varies depending on the OS of the server.
The number of volumes that can be created in the ETERNUS DX is shown below. Volumes can be created until the combined total for each volume type reaches the maximum number of volumes.
Model |
Maximum number of volumes (per RAID group) |
Maximum number of volumes (per storage system) |
|---|---|---|
ETERNUS DX600 S6 |
16,384 |
16,384 |
ETERNUS DX900 S6 ETERNUS DX8900 S6 |
65,535 |
65,535 |
A volume can be expanded or moved if required. Multiple volumes can be concatenated and treated as a single volume. For the availability of expansion, migration, and concatenation for each volume, refer to Target Volumes of Each Function.
The types of volumes that are listed in the table below can be created in the ETERNUS DX.
Type |
Usage |
Maximum capacity |
|---|---|---|
Standard (Open) |
A standard volume is used for normal usage, such as file systems and databases. The server recognizes it as a single logical unit. "Standard" is displayed as the type for this volume in ETERNUS Web GUI/ETERNUS CLI and "Open" is displayed in ETERNUS SF software. |
128TB (*1) |
Snap Data Volume (SDV) |
This area is used as the copy destination for SnapOPC/SnapOPC+. There is a SDV for each copy destination. |
24 [MB] + copy source volume capacity × 0.1 [%] (*2) |
Snap Data Pool Volume (SDPV) |
This volume is used to configure the Snap Data Pool (SDP) area. The SDP capacity equals the total capacity of the SDPVs. A volume is supplied from a SDP when the amount of updates exceeds the capacity of the copy destination SDV. |
2TB |
Thin Provisioning Volume (TPV) |
This virtual volume is created in a Thin Provisioning Pool area. TPVs are used as the copy destination for SnapOPC+. |
128TB |
Flexible Tier Volume (FTV) |
This volume is a target volume for layering. Data is automatically redistributed in small block units according to the access frequency. FTVs are used as the copy destination for SnapOPC+. An FTV belongs to a Flexible Tier Pool. |
128TB |
Virtual Volume (VVOL) |
A VVOL is a VMware vSphere dedicated capacity virtualization volume. Operations can be simplified by associating VVOLs with virtual disks. Its volume type is FTV. |
128TB |
Deduplication/Compression Volume |
This volume is a virtual volume that is recognized by the server when the Deduplication/Compression function is used. It can be created by enabling the Deduplication/Compression setting for a volume that is to be created. The data is seen by the server as being non-deduplicated and uncompressed. The volume type is TPV. |
128TB |
Wide Striping Volume (WSV) |
This volume is created by concatenating distributed areas in from 2 to 64 RAID groups. Processing speed is fast because data access is distributed. |
128TB |
ODX Buffer volume |
An ODX Buffer volume is a dedicated volume that is required to use the Offloaded Data Transfer (ODX) function of Windows Server 2012 or later. It is used to save the source data when data is updated while a copy is being processed. It can be created one per ETERNUS DX. Its volume type is Standard, TPV, or FTV. |
1TB |
| *1 | : | When multiple volumes are concatenated using the LUN Concatenation function, the maximum capacity is also 128TB. |
| *2 | : | The capacity differs depending on the copy source volume capacity. |
After a volume is created, formatting automatically starts. A server can access the volume while it is being formatted. Wait for the format to complete if high performance access is required for the volume.
In the ETERNUS DX, volumes have different stripe sizes that depend on the RAID level and the stripe depth parameter.
For details about the stripe sizes for each RAID level and the stripe depth parameter values, refer to "Web GUI User's Guide".
Note that the available user capacity can be fully utilized if an exact multiple of the stripe size is set for the volume size. If an exact multiple of the stripe size is not set for the volume size, the capacity is not fully utilized and some areas remain unused.
When a Thin Provisioning Pool (TPP) is created, a control volume is created for each RAID group that configures the TPP. Therefore, the maximum number of volumes that can be created in the ETERNUS DX decreases by the number of RAID groups that configure a TPP.
When the Flexible Tier function is enabled, 64 work volumes are created. The maximum number of volumes that can be created in the ETERNUS DX decreases by the number of work volumes that are created.
When a Flexible Tier Sub Pool (FTSP) is created, a control volume is created for each RAID group that configures the FTSP. Therefore, the maximum number of volumes that can be created in the ETERNUS DX decreases by the number of RAID groups that configure an FTSP.
When using the VVOL function, a single volume for the VVOL management information is created the moment a VVOL is created. The maximum number of volumes that can be created in the ETERNUS DX decreases by the number of volumes for the VVOL management information that are created.



