LUN Concatenation
LUN Concatenation is a function that is used to add new area to a volume and so expand the volume capacity available to the server. This function enables the reuse of leftover free area in a RAID group and can be used to solve capacity shortages.
Unused areas, which may be either part or all of a RAID group, are used to create new volumes that are then added together (concatenated) to form a single large volume.
The capacity can be expanded during an operation.
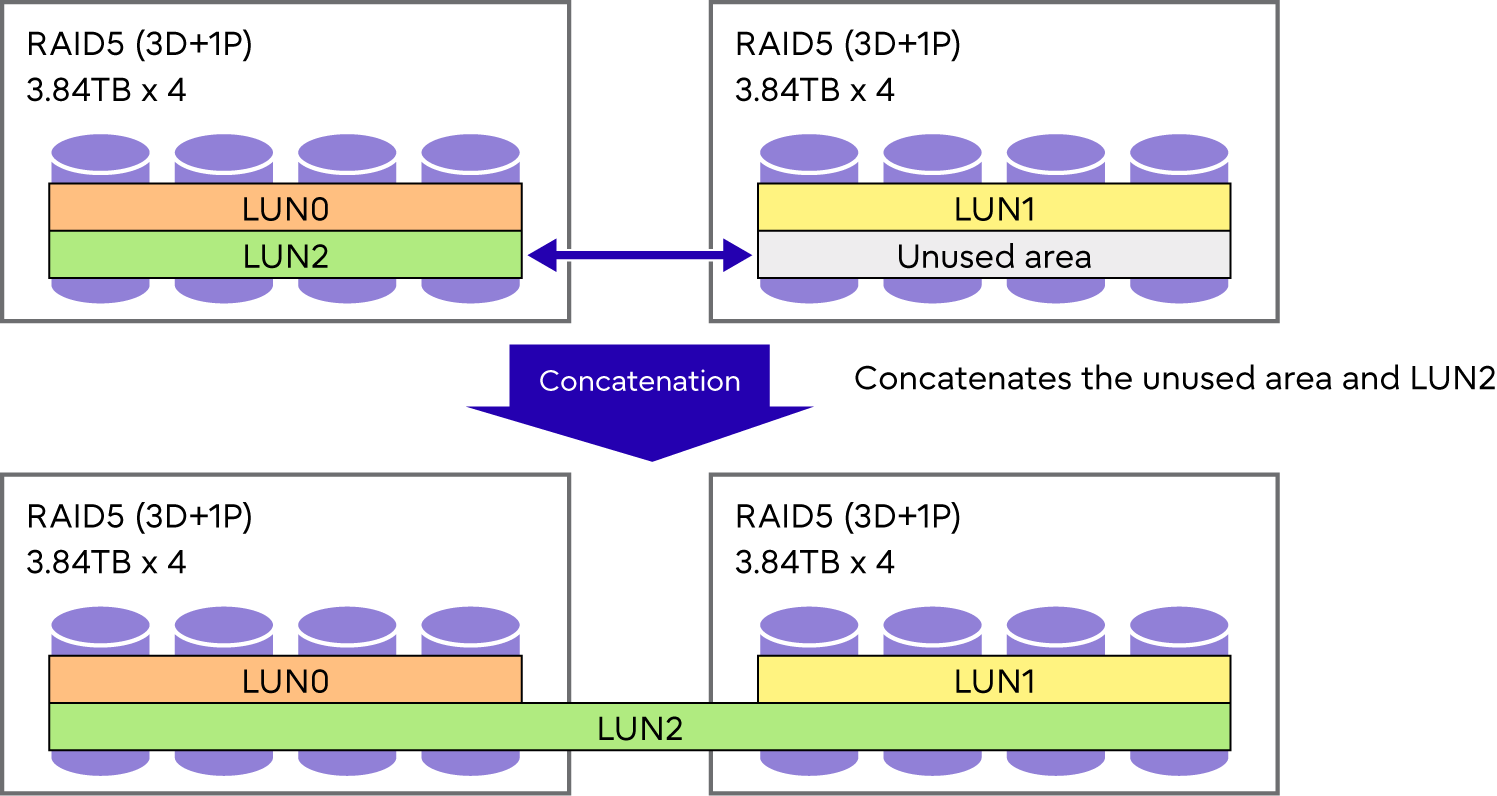
LUN Concatenation is a function to expand a volume capacity by concatenating volumes.
Up to 16 volumes with a minimum capacity of 1GB can be concatenated.
Volumes can be concatenated up to 128TB (up to 1TB for ODX Buffer volumes).
Concatenation can be performed regardless of the RAID levels of the concatenation source volume and the concatenation destination volume.
When there are concatenation source volumes in SAS disks or Nearline SAS disks, concatenation can be performed with volumes in SAS disks or Nearline SAS disks.
For NVMe SSDs, SAS SSDs, NVMe SSD SEDs, and SAS SSD SEDs, the drives for the concatenation source and destination volumes must be the same type (NVMe SSD, SAS SSD, NVMe SSD SED, or SAS SSD SED).
From a performance perspective, using RAID groups with the same RAID level and the same drives (type, size, capacity, or rotational speed [for disks]) is recommended as the concatenation source.
A concatenated volume can be used as an OPC, EC, or QuickOPC copy source or copy destination. It can also be used as a SnapOPC/SnapOPC+ copy source.
The LUN number stays the same before and after the concatenation. Because the server-side LUNs are not changed, an OS reboot is not required. Data can be accessed from the host in the same way regardless of the concatenation status (before, during, or after concatenation). However, the recognition methods of the volume capacity expansion vary depending on the OS types.
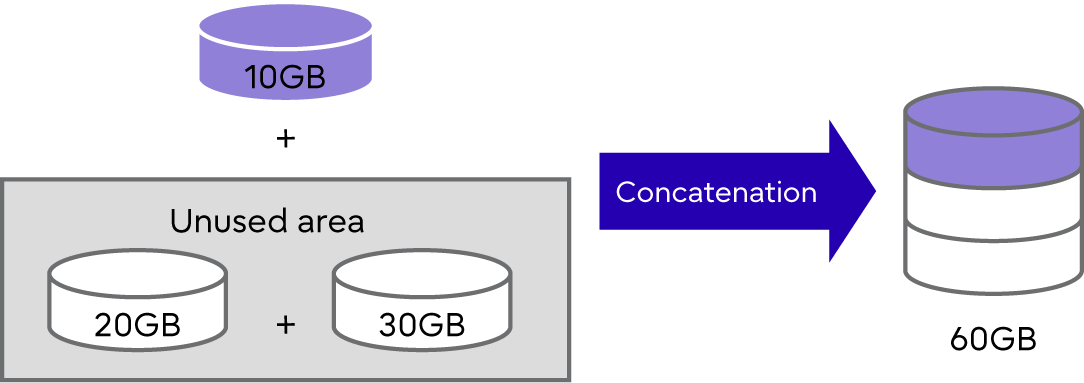
Only Standard type volumes can be used for LUN Concatenation. The encryption status of a concatenated volume is the same status as a volume that is to be concatenated.
LUN Concatenation may not be available when other functions are being used in the ETERNUS DX or the target volume.
For details on the functions that can be executed simultaneously, refer to Combinations of Functions That Are Available for Simultaneous Executions.
It is recommended that the data on the volumes that are to be concatenated be backed up first.
Refer to the applicable OS and file system documentation before dynamically expanding the volume capacity because expanded volumes may not be recognized by some types and versions of server-side platforms (OSs).
When a volume that is using ETERNUS SF AdvancedCopy Manager to run backups is expanded via LUN Concatenation, the volume will need to be registered with ETERNUS SF AdvancedCopy Manager again.
When specifying a volume in the RAID group configured with Advanced Format drives as a concatenation source or a concatenation destination to expand the capacity, the write performance may be reduced when accessing the expanded volumes from an OS or an application that does not support Advanced Format.



