Wide Striping
Wide Striping is a function that concatenates multiple RAID groups by striping and uses many drives simultaneously to improve performance. This function is effective when high random write performance is required.
I/O accesses from the server are distributed to multiple drives by increasing the number of drives that configure a LUN, which improves the processing performance.
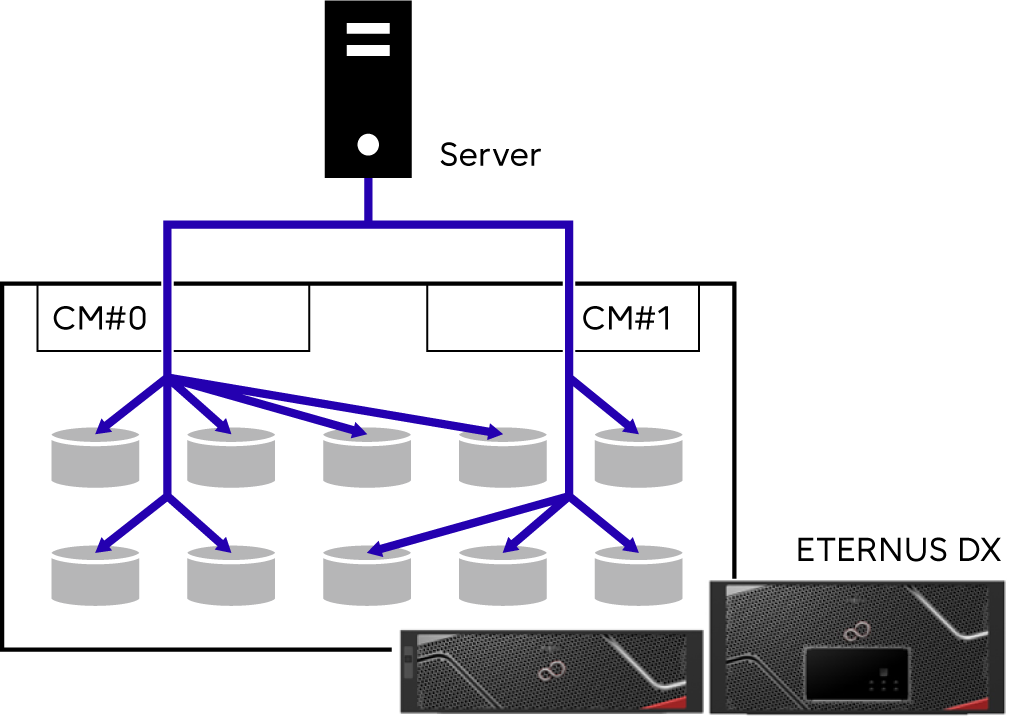
Wide Striping creates a WSV that can be concatenated across 2 to 64 RAID groups.
The number of RAID groups that are to be concatenated is defined when creating a WSV. To change the number of concatenated groups or expand the capacity of RAID groups after a WSV is created, perform RAID Migration.
Volumes can be concatenated up to 128TB.
Other volumes (Standard volumes, SDVs, SDPVs, or WSVs) can be created in the free area of a RAID group that is concatenated by Wide Striping.
WSVs are created by concatenating RAID groups that have the same state with regard to the following conditions.
RAID level
Number of member drives
Stripe depth
Type of drive to be configured and rotational speed (for disks)
WSVs cannot be created in the following RAID groups.
RAID groups that belong to TPPs or FTRPs
RAID groups that are registered as REC Disk Buffers
RAID groups that are registered as Extreme Cache Pools
RAID groups that are configured with RAID6-FR
RAID groups without a continuous free area greater than the capacity of the volumes to be concatenated
Capacity expansion cannot be performed (LDE is not possible) for RAID groups used to configure a WSV.
If one or more RAID groups that are configured with Advanced Format drives are to be concatenated by striping to create a WSV, the write performance may be reduced when accessing the created WSVs from an OS or an application that does not support Advanced Format.



