SANtricity express configuration manuals ( CA08872-012 )
Points to Note with SANtricity
Points to Note when using the ETERNUS AB/HB series
Notes Related to Linux iSCSI Connections
If a command is issued to a disk device that is connected to a server via iSCSI, response delays occur for the command and performance degradation problems may occur. As a connection configuration example, if a mixed network is used, such as an iSCSI network with a management LAN network, the occurrence of problems tends to increase. This can be improved by disabling delayed ACK. However, depending on the type of Linux OS, disabling delayed ACK may not be possible. For information on how to disable it, refer to the Linux OS manual.
Notes Related to Access Volumes
Volumes referred to as access volumes are automatically created for the ETERNUS AB2100, ETERNUS AB5100, ETERNUS HB1100/HB1200/HB1300/HB1400, ETERNUS HB2100/HB2200/HB2300/HB2400/HB2500/HB2600, and ETERNUS HB5100/HB5200. Although access volumes are necessary volumes when the automatic host creation and in-band management functions are used, those functions are not supported by our storage. Delete LUN mapping for the access volumes. To delete LUN mapping, perform Storage > Hosts > Unassign Volumes from SANtricity System Manager, or execute the "remove lunmapping" command from SMcli. For details, refer to ETERNUS AB/HB series SANtricity commands: Commands A-Z".
Notes Related to iSCSI Connections of VMware ESXi Servers
If a command is issued to a disk device that is connected to a server via iSCSI, response delays occur for the command and performance degradation problems may occur.
As a connection configuration example, if a mixed network is used, such as an iSCSI network with a management LAN network, the occurrence of problems tends to increase.
This can be improved by disabling delayed ACK. However, depending on the type of Linux OS, disabling delayed ACK may not be possible. For information on how to disable it, refer to the Linux OS manual.
Notes Related to the Jumbo Frame Setting
VMware
-
To enable Jumbo Frame, all the connected devices must support Jumbo Frame. Set an appropriate value for the various parameters (such as MTU size) of the connected devices.
-
For the Jumbo Frame setting method of devices such as LAN cards and Ethernet switches, refer to the manuals of VMware ESXi and the various devices. To reflect the setting, the server may require a restart.
-
The MTU sizes supported by the ETERNUS AB/HB series are between 1,500 to 9,000 bytes. (Default MTU size: 1,500 bytes/frame)
Notes Related to the Ethernet Switch Setting
VMware, Windows, and Linux
Configure the Ethernet switch by keeping the following points in mind.
-
High availability is ensured by using two networks. Separate iSCSI traffic into different networksegments.
-
Hardware flow control is enabled for the servers and switches. In addition, priority flow control is disabled.
-
Jumbo Frame is enabled when necessary.
To enable Jumbo Frame, it must be set for the servers, switches, and storage systems. For the storage systems, refer to the following manual to set an appropriate MTU value.
Notes Related to FC Connections of VMware ESXi Server
VMware
If NVMe support is enabled during an FC connection, duplicate WWPNs may be displayed.
During an FC connection, disabling NVMe support is recommended.
For details on how to disable NVMe support, refer to the following Broadcom website.
https://knowledge.broadcom.com/external/article?legacyId=84325
-
For the lpfc Driver
-
Execution example 1
# esxcli system module parameters set -m lpfc -p "lpfc_enable_fc4_type=1 lpfc0_lun_queue_depth=8"
When changing the value of the driver parameter "lpfcX_lun_queue_depth", disable NVMe support at the same time. Even if NVMe support is already disabled and the "lpfcX_lun_queue_depth" value is changed later, disable NVMe support every time.
-
Execution example 2
# esxcli system module parameters set -m lpfc -p lpfc_enable_fc4_type=1
Disable NVMe support.
# esxcli system module parameters set -a -m lpfc -p lpfc0_lun_queue_depth=8
Change the value of the driver parameter "lpfcX_lun_queue_depth". By specifying the "-a" option, the "lpfcX_lun_queue_depth" value is changed but the NVMe support remains disabled.
-
-
For the qlnativefc Driver
-
Execution example 1
# esxcli system module parameters set -m qlnativefc -p "ql2xnvmesupport=0 ql2xmaxqdepth=8"
When changing the value of the driver parameter "ql2xmaxqdepth", disable NVMe support at the same time. Even if NVMe support is already disabled and the "ql2xmaxqdepth" value is changed later, disable NVMe support every time.
-
Execution example 2
# esxcli system module parameters set -m qlnativefc -p ql2xnvmesupport=0
Disable NVMe support.
# esxcli system module parameters set -a -m qlnativefc -p ql2xmaxqdepth=8
Change the value of the driver parameter "ql2xmaxqdepth". By specifying the "-a" option, the "ql2xmaxqdepth" value is changed but the NVMe support remains disabled.
-
Notes Related to VMware ClusteredVMDK
The ETERNUS AB/HB series does not support VMware ClusteredVMDK.
Notes Related to FC Connections of VMware ESXi Server
-
VMware vSphere 8.0
-
VMware vSphere 7.0
In the VMware Guest OS, frequent I/O errors occur in the storage system.
If I/O errors such as system errors and file system errors occur frequently, in rare cases it may cause a kernel panic, and the VMware Guest OS may be stopped as a result.
Disk timeout value for VMware Guest OS may be incorrect.
These phenomena may occur when a storage system is suspended for a short period of time (such as a path failover) during normal operation, and when the suspend time exceeds the disk timeout value of the VMware Guest OS.
If an incorrect disk timeout value is specified for VMware Guest OS, change (manually increase) the disk timeout value to avoid or reduce errors. This may prevent the VMware Guest OS from stopping due to a kernel panic.
Notes Related to Path Selection Policy on VMware
If the Path Selection Policy is set to "Most Recently Used (VMware)", change "Path Selection Policy" of all storage devices (LUN) to "Round Robin (VMware)". Commands can be used to check and set it.
# esxcli storage nmp satp rule list -s VMW_SATP_ALUA
# esxcli storage nmp satp rule add -s VMW_SATP_ALUA -V FUJITSU -M ETERNUS_AHB -c tpgs_on -P VMW_PSP_RR -e "Fujitsu Eternus arrays with ALUA support"
Notes Related to Enabling Auto Load Balancing (ALB) on VMware
VMware
In a VMware standard Native Multipathing Plug-in (NMP) environment, the path disconnects during an owner change when the Auto Load Balancing (ALB) function is operating while Auto Load Balancing is enabled in the ETERNUS AB/HB series.
This is the operation specification for the combination of NMP and ALB.
By applying the VMware Multi-Pathing plug-in for ETERNUS AB/HB series, the path disconnection that occurs during an owner change when the ALB function is operating can be avoided.
Notes Related to Applying VMware Multi-Pathing plug-in for ETERNUS AB/HB
VMware
| Contact your our company sales representative to obtain support for this software. |
When the ETERNUS AB/HB series is added to the configuration, applying VMware Multi-Pathing plug-in for ETERNUS AB/HB is recommended to manage the non-response state due to a slowdown of the VMware ESXi host when intermittent faults occur in the path.
Use the latest supported version of the module for the VMware ESXi version being used.
The functional overview and functional enhancement details of VMware Multi-Pathing plug-in for ETERNUS AB/HB are described below.
-
Functional Overview
VMware Multi-Pathing plug-in for ETERNUS AB/HB is a sub plug-in of the VMware standard Native Multipathing Plug-in (NMP) used to configure multipath connections with ETERNUS storage systems.
It is also used as a Storage Array Type Plug-in (SATP) to perform error handling controls that correspond to ETERNUS storage systems. -
Details about Functional Enhancements
In addition to the normal multipath functions, the path switching function that triggered in 1 to 3 below is supported.
This may reduce phenomena such as host becoming unresponsive because the path is not switched, so applying VMware Multi-Pathing plug-in for ETERNUS AB/HB is recommended.-
Switching the path when it is unresponsive
Paths are switched when the I/O is unresponsive.
-
Enhanced diagnosis of dead paths
Paths are recovered after confirming that normal response continues for at least 20 minutes during the diagnosis.
By preventing rapid recovery of the paths with the intermittent faults, the system slowdown time can be reduced.
In an environment that does not use VMware Multi-Pathing plug-in for ETERNUS AB/HB, paths are recovered when the diagnosis succeeds just a single time. -
Blocking unstable paths
If the path status changes from "online" to "dead" six times within three hours after the first
status transition, the path is recognized as being unstable and the status is changed to "fataldead". The "fataldead" state is not recovered with a diagnosis, but can be recovered by
executing a command manually.The command is described in Software Information (readme.txt), which is included in the downloaded module. Check the VMware Multi-Pathing plug-in for ETERNUS AB/HB support status.
This can prevent the continued slowdown state even if step2 cannot manage the paths with the intermittent fault.
In an environment that does not use VMware Multi-Pathing plug-in for ETERNUS AB/HB, no functions are available to detect unstable paths.
-
For procedure to download this software, contact our sales representative.
Notes Related to the Installation of Windows Host Utilities 7.1 to Windows Server 2019
If MPIO (OS standard multipath driver) is not enabled, installation of Windows Host Utilities 7.1 to Windows Server 2019 may fail.
Even for single path configurations, install SANtricity Windows DSM and enable the multipath function.
Notes Related to Disk Timeouts on Virtual Machines Running on Hyper-V
To set the disk I/O timeout in a virtual machine that is running on Hyper-V, modify and set the following registry key. The disk timeout must be set to a minimum of 180 seconds.
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\\SYSTEM\\CurrentControlSet\\Services\\Disk] \TimeOutValue\
When specifying 180 seconds, add the following line.
\TimeOutValue\=dword:000000b4
Notes Related to Upgrading the SANtricity OS Software in Hyper-V Environments for Windows Server 2016 and Later
FC (vFC), iSCSI, and SAS
If the SANtricity OS software upgrade is executed, virtual machines that have virtual disks mapped through Hyper-V may lose I/O access. However, commands sent to the physical path are usually held by Windows Server (OS) for 75 seconds.
The workaround is to stop the virtual machine before the SANtricity OS software upgrade.
It is restored if the virtual machine is restarted.
Notes Related to Connections with a Windows Server
-
Windows Server (including Hyper-V and Windows Server used with Guest OS in a virtual environment)
-
ETERNUS AB/HB series
-
FC/iSCSI/SAS/NVMe
-
Direct connection or connection via a switch
-
SAN connections (Localboot/SANboot)
If Windows Server and the ETERNUS AB/HB series are connected, and when Windows Server is rebooted after the SANtricity OS software is applied to the storage system, the status of the disks on Windows Server may become offline.
-
Checking the Disk Status
Use the following procedure to check the disk status on Windows Server.
-
Click Start and select Management Tool > Computer Management .
-
Open Disk Management in the left pane to check the disk state.
-
Windows Server uses the edition number of SANtricity OS provided by the storage system as a disk ID (instance ID). This occurs according to the specifications of Windows Server. When the OS is started, if the instance ID of the disk has been changed, the OS recognizes the disk as a new disk.
In addition, the disk status is set at system startup. The status that is set varies depending on the path configuration.
-
For single path configurations
The disk status is determined according to the SAN Policy settings.
-
For multipath configurations
The disk status (online or offline) before configuring the multipath is taken over regardless of theSAN Policy settings.
For the edition number of SANtricity OS of the ETERNUS AB/HB series, the version that has been changed by updating SANtricity OS is returned. This changes the ID information of disks and causes this phenomenon.
The occurrence condition and the workaround differ depending on the path configuration of Windows Server.
To prevent the disk in single-path configurations from going offline after the SANtricity OS software is applied, temporarily change the SAN Policy setting before applying the SANtricity OS software.
For multipath configurations, there is no workaround. The procedure in Recovery Method After Problems Occur must be performed to recover from the offline status.
The workaround for each configuration is described below.
-
For Single Path Configurations
The offline status can be avoided by changing the SAN Policy setting to "Online All" only when upgrading the SANtricity OS software. If operations are possible with the SAN Policy setting set to "Online All", Step 4 is not required. The following describes the workaround.
-
Check the current SAN Policy settings.
-
Execute the "diskpart" command in the command prompt.
-
The prompt changes as shown below. Enter "san" and press the [Enter] key.
Execution example
DISKPART> san
-
One of the following SAN Policies appears.
-
Offline Shared
-
Offline All
-
Online All
-
-
Record the current setting value.
The recorded value is used in Step 4 to restore the SAN Policy setting.
-
-
Change the SAN Policy setting.
-
Confirm that the prompt is "DISKPART", enter "san policy=onlineall" and press the [Enter] key.
Execution example
DISKPART> san policy=onlineall
-
To apply the changed SAN Policy settings, reboot Windows Server.
-
Execute the "diskpart" command in the command prompt again and confirm that the SAN Policy is set to "Online All".
Execution example
DISKPART> san SAN Policy : Online All
-
-
Upgrade the SANtricity OS software.
-
Upgrade the SANtricity OS software in the ETERNUS AB/HB series.
-
To get OS to recognize the new instance ID, reboot Windows Server.
-
-
Restore the SAN Policy setting.
-
Restore the SAN Policy setting to the previous value.
Execution example
DISKPART> san policy=Offline Shared
To apply the SAN Policy setting, reboot Windows Server.
-
Execute the "diskpart" command again in the command prompt and confirm that the previous value is specified for the SAN Policy setting.
Execution example
DISKPART> san SAN Policy : Offline Shared
-
-
-
For Multipath Configurations
When the multipathing of an online disk is set up during the configuration of the environment, the multipath disk starts up in online status after the SANtricity OS software is upgraded. This is because the disk status immediately prior to configuration of the multipath is inherited.
When the multipathing of an offline disk is set up, the multipath disk starts up in offline status after the SANtricity OS software is upgraded. There are no measures that can be taken (such as a setting change) to prevent the disk from going offline after the environment is configured. Perform the procedure described in Recovery Method After Problems Occur if the disk status is offline after the SANtricity OS software upgrade.
-
When the OS Can Be Started Up
Manually change the offline disks to online by following the procedure below.
-
Click Start and select Management Tool > Computer Management.
-
Select each offline disk in Disk Management, then right-click the selected disk to change the status to online.
-
-
When the OS Cannot Be Started Up
If the Active Directory database is located in a disk other than the OS area, the OS may not be able to start up because the disk is offline and the OS cannot access the Active Directory database.
In this case, the disk can be recovered by starting the OS in the Directory Services Restore Mode and changing the disk status to online.
The procedure for recovering is as follows:-
Start the server.
-
Press the [F8] key on the server start-up screen.
-
The Advanced Boot Options screen appears.
-
Select Directory Services Restore Mode.
-
Log in as Administrator after the OS starts.
-
Select [Management Tool] > [Computer Management].
-
Select each offline disk in [Disk Management], then right-click the selected disk to change the status to online.
-
Restart the OS.
-
Notes Related to Windows Server iSCSI Connections (Including Hyper-V Environments)
If a command is issued to a disk device that is connected to a server via iSCSI, response delays occur for the command and performance degradation problems may occur.
This can be improved by disabling delayed ACK. For information on how to disable it, refer to the Windows Server manual.
Notes Related to the Disk Driver for Oracle Solaris
In Solaris 11.4, the disk driver used in the FC or iSCSI connected storage system has changed from ssd to sd. In Solaris 11.3 and earlier, the parameter set to ssd must be changed to sd.
| If an OS that is Solaris 11.3 or earlier is updated to Solaris 11.4, because the ssd driver will still be used, problems will not occur. |
Because the settings content is not valid for the following, problems may occur.
-
The ssd driver parameter is set the same as before
-
The sd driver is not reassigned to the ssd driver
In addition, it may be affected by the parameters for the sd driver set for the internal disk. As a result, business may be suspended.
-
Target servers
-
SPARC Enterprise
-
SPARC Servers
-
-
Target OS
-
Solaris 11.4
-
The following is comparison information between OS versions when a storage system is used.
| Item | Solaris 11.3 | Solaris 11.4 |
|---|---|---|
Driver name |
ssd |
sd |
Physical device name |
/pci@ ~ |
/pci@ ~ |
Instance name |
ssd1 |
sd1 |
Parameter |
Definition file: |
Definition file: |
Definition file: |
Definition file: |
Depending on the environment and requirements, the storage device (our storage, non-our storage, or virtual storage) that is connected using FC or iSCSI will not work as expected and the setting may not be valid.
An example of the phenomenon is shown below.
| For iSCSI, an MPxIO connection is a requirement. |
-
Phenomenon 1
During a path failure of a multipath configuration, the path may take time to switch and I/O may slow down.
-
Environment
The storage system is connected using FC or iSCSI and the multipath is configured using the Oracle Solaris standard multipath driver (MPxIO).
-
Occurrence Conditions
A Solaris 11.4 OS is newly installed and the parameter for the ssd driver is used to perform a storage system configuration.Configuration example to the /etc/system file
set ssd:ssd_io_time = 20 set ssd:ssd_max_throttle = 8
-
-
Phenomenon 2
If a load that exceeds the processing performance is applied when a our storage system is connected, the performance is significantly reduced and I/O slows down.
Note that for non-our storage systems, in addition to significant performance reduction and I/O slowdown, I/O hang ups also occur.
-
Environment
The storage system is connected using FC or iSCSI.
-
Occurrence Conditions
A Solaris 11.4 OS is newly installed and the parameter for the ssd driver is used to perform a storage system configuration.Configuration example to the /etc/system file
set ssd:ssd_io_time = 20 set ssd:ssd_max_throttle = 8
-
-
Phenomenon 3
I/O to the storage system quickly times out and takes time.
-
Environment
The storage system is connected using FC or iSCSI and the internal disks are configured with sd driver parameters. This parameter can be set when using PRIMECLUSTER GD.
Configuration example to the /etc/system file
set sd:sd_io_time = 30 (the default for Oracle Solaris is 60 seconds)
-
Occurrence Conditions
A Solaris 11.4 OS is newly installed and the parameter for the ssd driver is used to perform a storage system configuration.Configuration example to the /etc/system file
set ssd:ssd_io_time = 20 set ssd:ssd_max_throttle = 8
-
-
How to Prevent Problems from Occurring
-
For Phenomena 1 to 3
For the parameter set in the ssd driver as below, it is changed to the sd driver parameter.
Item Pre-change Post-change Configuration file
/etc/system
(Common file for the sd and ssd drivers)No change due to commonality
Configuration parameter
ssd_io_time
sd_io_time
ssd_max_throttle
sd_max_throttle
Item Pre-change Post-change Configuration file
/etc/driver/drv/ssd.conf
/etc/driver/drv/sd.conf
Configuration parameter
ssd-config-list
sd-config-list
Note that for Solaris 11.4 and later, the sd driver parameter is a common parameter for internal disks and storage systems. If different parameter settings are required for both the internal disk and the storage system, each can be set in the following files.
-
Internal disk: /etc/system file
-
Storage system: /etc/driver/drv/sd.conf file
When the parameter set in /etc/system is set in /etc/driver/drv/sd.conf, the correspondence is as follows.
Item Pre-change Post-change Configuration file
/etc/system
/etc/driver/drv/sd.conf
Configuration parameter
sd_io_time
cmd-timeout in sd-config-list
sd_max_throttle
throttle-max in sd-config-list
For details of the sd-config-list parameter, refer to the following Oracle website.
https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E53394_01/html/E54792/
Reference: "Appendix C Tuning Disk Target Driver Properties"
-
-
-
Recovery Method After Problems Occur
If the system hangs up, follow the model-specific procedure to force a panic and restart the system. After that, perform How to Prevent Problems from Occurring, How to Prevent Problems from Occurring. The forced panic instructions are included in the operation for collecting the crash dump during a hang up. Note that if an investigation is not performed, the collected crash dump can be deleted.
Notes Related to iSCSI Connections of Oracle Solaris
-
Workaround
Use the following command to change the conn-login-max value in the iSCSI initiator to "60".
# iscsiadm modify initiator-node -T conn-login-max=60
Notes Related to Automatic Load Balancing of Oracle Solaris
Oracle Solaris does not support Automatic Load Balancing. Therefore, the Automatic Load Balancing function does not work even though it is enabled by default. However, when using a multipath diagnostic program, make sure to disable Automatic Load Balancing.
Notes Related to the Volume Relocation of Oracle Solaris
Even if a volume redistribution is performed from SANtricity System Manager, the preferred controller owner may not return for some volumes.
-
Impact on the Business
In Recovery Guru of SANtricity System Manager, "Volume Not On Preferred Path" is displayed.
An equivalent I/O performance prior to the occurrence of the phenomenon may not be obtained. -
Details of the Phenomenon
If the Environment and Occurrence Conditions described later are satisfied, the Access State on the preferred path side does not return to "active optimized" using the Solaris standard Multipath (MPxIO).
If this phenomenon occurs, "Volume Not On Preferred Path" is displayed in RecoveryGuru of SANtricity System Manager.The Access State can be confirmed with the following command.
Example:
# mpathadm show lu /dev/rdsk/c0t6D039EA00018A6CB00001B17621FF20Bd0s0
Logical Unit: /dev/rdsk/c0t6D039EA00018A6CB00001B17621FF20Bd0s2
mpath-support: libmpscsi_vhci.so
Vendor: FUJITSU
Product: ETERNUS_AHB
Revision: 0871
(omitted)
Target Port Groups:
ID: 1
Explicit Failover: yes
Access State: active not optimized
Target Ports:
Name: 2015d039ea18a991
Relative ID: 32769
ID: 0
Explicit Failover: yes
Access State: active optimized
Target Ports:
Name: 2014d039ea18a991
Relative ID: 1
-
Environment
Occurs when all the following conditions are satisfied.
-
An ETERNUS AB/HB series is connected.
To check whether the server is connected to the ETERNUS AB/HB series, use the following command. If it is connected to the ETERNUS AB/HB series, "ETERNUS_AHB" is displayed in "Product:"
# mpathadm show lu /dev/rdsk/c0t6D039EA00018A6CB00001B17621FF20Bd0s0 Logical Unit: /dev/rdsk/c0t6D039EA00018A6CB00001B17621FF20Bd0s2 mpath-support: libmpscsi_vhci.so Vendor: FUJITSU Product: ETERNUS_AHB -
The storage system in (1) is connected using the Solaris standard Multipath (MPxIO).
-
The Multipath Diagnostic Program is being used.
To check whether the Multipath Diagnostic Program is being used, use the following command. It is in use if "fjsvpdiagAHBX" processes are displayed using grep
# ps -ef|grep fjsvpdiagAHBX root 27408 27407 0 15:53:50 0:00 /opt/FJSVpdiag/bin/fjsvpdiagAHBX root 27407 1 0 15:53:50 0:00 /opt/FJSVpdiag/bin/fjsvpdiagAHBX
-
-
Occurrence Conditions
When a volume redistribution is performed from SANtricity System Manager.
-
Cause
If "Redistribute volumes" is performed from SANtricity System Manager of the ETERRNUS AB/HB series, a sense notification is sent to the server from the ETERNUS AB/HB series seires. In an environment in which the Multipath Diagnostic Program is not running, the MPxIO receives the sense for the I/O it issued and switches the path status. However, if the Multipath Diagnostic Program is running, the sense may be received for the diagnostic I/O that is issued by the program without notifying the sense to the MPxIO and the state cannot return to the Access State.
-
How to Prevent Problems from Occurring
Before the redistribution, stop the diagnostic program.
Execution example:
-
Confirm that a redistribution can be performed.
In SANtricity System Manager, make sure Preferred Owner and Current Owner are different.
Preferred Owner Current Owner Volume01
Controller A
Controller B
Volume02
Controller A
Controller B
If the volumes in [Preferred Owner] and [Current Owner] are different as in the above table, a redistribution can be performed. For information on how to perform the operation in SANtricity System Manager, check the manuals such as the online help.
-
Stop the Multipath Diagnostic Program.
-
Execute the following command as the root user.
# /opt/FJSVpdiag/etc/S99pdiagAHBX stop
-
Make sure there are no resident processes (/opt/FJSVpdiag/bin/fjsvpdiagAHBX) running.
Example:
# ps -ef | grep fjsvpdiagAHBX
-
-
Execute "Redistribution" from SANtricity System Manager.
For information on how to perform the operation in SANtricity System Manager, check the manuals such as the online help.
-
Confirm the Access State.
Confirm that the Access State on the preferred path is "active optimized" for all the volumes.
-
Confirm the Access State with the "mpathadm" command.
Execution example for mpathadm:
# mpathadm show lu /dev/rdsk/c0t6D039EA00018A6CB00001B17621FF20Bd0s0 Logical Unit: /dev/rdsk/c0t6D039EA00018A6CB00001B17621FF20Bd0s2 mpath-support: libmpscsi_vhci.so Vendor: FUJITSU Product: ETERNUS_AHB Revision: 0871 (omitted) Target Port Groups: ID: 1 Explicit Failover: yes Access State: active not optimized (*1) Target Ports: Name: 2015d039ea18a991 (*2) Relative ID: 32769 ID: 0 Explicit Failover: yes Access State: active optimized (*3) Target Ports: Name: 2014d039ea18a991 (*4) Relative ID: 1In the above example, the "active optimized" (3*) port of the logical unit
/dev/rdsk/c0t6D039EA00018A6CB00001B17621FF20Bd0s2is the target port whose ID is0and Name is2014d039ea18a991(4*). Use SANtricity System Manager to confirm that this path is Preferred Owner and Current Owner.*1: Path notation on the controller side that does not have preferred ownership
*2: World Wide Port Identifier on the controller side that does not have preferred ownership
*3: Path notation on the controller side that has preferred ownership
*4: World Wide Port Identifier on the controller side that has preferred ownership
-
Check which controller side is the active optimized (*5) path.
Click the following in order in Hardware of SANtricity System Manager.
Show front of shelf > Controller A or Controller B > View settings > Host interfaces > Show more settings In the displayed Fibre Channel host ports, scroll right to World Wide Port Identifier and search for Target Ports: Name (*6).*5: The controller side that has preferred ownership
*6: World Wide Port Identifier on the controller side that has preferred
ownership -
Open the [Volume Settings] screen of Logical Unit.
In Storage > Volumes, select the corresponding volume, and click View/Edit Settings to open Volume Settings.
If the volume name that corresponds to Logical Unit is not known, find it with the following procedure.
In Storage > Volumes, select the volumes in order from the top, and click View/Edit Settings to open Volume Settings.
Find the volume that matches both the World-Wide Identifier (WWID) of the Volume Settings screen (excluding ":") and the Logical Unit shown by the
mpathadmcommand (excluding/dev/rdsk/c0tandd0s2).If Logical Unit and World-Wide identifier (WWID) are displayed as below, it is the corresponding volume.
Example:
Logical Unit: /dev/rdsk/c0t6D039EA00018A6CB00001B17621FF20Bd0s2 World-Wide Identifier (WWID) : 6D:03:9E:A0:00:18:A6:CB:00:00:1B:17:62:1F:F2:0B
-
In [Controller ownership] of [Advanced] on the [Volume Settings] screen, confirm that both preferred owner and current owner match the controller in Step 4-b. If they differ, "Redistribute volumes" may have failed.
However, it may take 10 to 15 minutes before the latest Access State applied if there is no I/O access. Wait 15 minutes and try again from Step 4 (Confirm the Access State).
-
-
Start the Multipath Diagnostic Program.
-
Execute the following command as the root user.
# /opt/FJSVpdiag/etc/S99pdiagAHBX
-
Confirm that the resident processes
/opt/FJSVpdiag/bin/fjsvpdiagAHBXare running.# ps -ef | grep fjsvpdiagAHBX root 10303 10302 0 17:53:52 ? 0:00 /opt/FJSVpdiag/bin/fjsvpdiagAHBX root 10302 1 0 17:53:52 ? 0:00 /opt/FJSVpdiag/bin/fjsvpdiagAHBX
-
-
-
Recovery Method After Problems Occur
Refer to How to Prevent Problems from Occurring, and perform the volume relocation again.
Notes Related to Configurations Where a Server Is Connected to a Single Controller Only
For configurations where a server is connected to a single controller only, errors are output (by Recovery Guru). However, only errors are output and there is no effect on the operation of the storage system.
The following errors are output.
-
Host Redundancy Lost
-
Host Multipath Driver Incorrect
-
Volume Not On Preferred Path
To prevent the errors from being output, set the Automatic Load Balancing to disable and the host connectivity report to disable.
Notes Related to the Maximum Number of Commands That Can Be Processed Simultaneously (Queue Depth)
The maximum number of commands that can be processed simultaneously (Queue Depth) is 2,048 per controller. Set this value on the server side so that the maximum value is not exceeded. For the setting method, refer to the server manual.
Notes Related to LAN Environments
Environments where the iSCSI LAN is not configured with a dedicated network have the following effects.
-
Processing delays may occur on mutual networks due to traffic conflicts.
-
In terms of security, problems such as SAN data leakage may occur.
Configure the iSCSI LAN so that it is on a dedicated network by separating the IP address segment from the business LAN and the administration LAN (such as separating the paths physically or in the VLAN).
Notes Related to Server Connections for Oracle Solaris
If a load consolidation occurs in the controllers that control the volumes in the server connected to the ETERNUS AB/HB series, the preferred controller owner may not be automatically returned.
The following example conditions show when a load consolidation occurs:
-
When servers and switches fail
-
When the connected cables fail or are disconnected
-
When a path is switched from the server
-
When SANtricity OS is upgraded
Oracle Solaris
The following phenomena occur.
The "Volume Not On Preferred Path" message appears in Recovery Guru of SANtricity System Manager.
If there are some volumes whose preferred controller owner has not been returned, an equivalent I/O performance prior to the occurrence of the phenomenon may not be obtained.
-
Impact on the Business
The data access performance may be reduced.
-
Environment
Server OS SPARC Enterprise
SPARC ServersSolaris
-
Occurrence Conditions
This phenomenon occurs when multipath is configured and the controller that controls volumes in an Oracle Solaris environment is load-consolidated.
-
Cause
This occurs due to the specified behavior in the ETERNUS AB/HB series when Oracle Solaris standard multipath driver (MPxIO) is used.
-
How to Prevent Problems from Occurring
There is no workaround.
-
Recovery Method After Problems Occur
Execute the "Redistribute volumes" function on SANtricity System Manager of the ETERNUS AB/HB series.
Perform the following procedure.
-
Access SANtricity System Manager and select Storage > Volumes.
-
Select More > Redistribute volumes.
-
In the Redistribute volumes screen, enter redistribute and execute the command.
-
|
For the descriptions about each function, the checking method of the setting, and the details about the procedure, refer to Redistribute volumes When using Oracle Solaris, also check Notes Related to the Volume Relocation of Oracle Solaris. |
Notes for PRIMECLUSTER Configurations
The following PRIMECLUSTER functions and configurations are not supported.
-
I/O fencing
-
Mirroring between disk storage systems
-
Optional products for PRIMECLUSTER GD (PRIMECLUSTER GD Snapshot and PRIMECLUSTER GD I/O Monitor Option)
Notes for Redundant Path Configurations
To configure multiple host interfaces that exist in a server with redundant paths, both controllers must be connected and configured with the same number of paths in Host Settings to maintain controller redundancy.
If the controllers used for host access paths are not evenly distributed, the following errors are output.
-
Host Redundancy Lost
-
Host Multipath Driver Incorrect
-
Volume Not On Preferred Path
Notes Related to Hosts and Host Clusters
The ETERNUS AB/HB series does not support the following.
-
Automatic creation of hosts
-
In-band management
Notes Related to iSCSI 25Gbps/10Gbps Connections
The ETERNUS AB/HB series where 25Gbps/10Gbps iSCSI host interface cards (HICs) are installed
| Onboard iSCSI ports are excluded. |
-
25Gbps/10Gbps iSCSI switches
-
25Gbps/10Gbps iSCSI converged network adapters (CNAs) or 25Gbps/10Gbps iSCSI network interface cards (NICs)
The 25Gbps/10Gbps iSCSI host interface card (HIC) in the ETERNUS AB/HB series may not connect to the host via iSCSI connections.
The 25Gbps/10Gbps iSCSI host interface card (HIC) in the ETERNUS AB/HB series does not support auto negotiation or the Forward Error Correction (FEC) of the auto negotiation.
-
Specify the communication speed of the 25Gbps/10Gbps iSCSI host interface card (HIC) as the required fixed value using SANtricity System Manager of the ETERNUS AB/HB series. To do so, perform the following procedure.
-
Access SANtricity System Manager and select Settings > System.
-
Select iSCSI settings > Configure iSCSI ports.
-
Select Controller A or Controller B and click Next.
-
Select an interface (such as
HIC 1, Port 0c) on the host interface card (HIC) and click Next. -
From the Configured ethernet port speed drop-down list, select
25Gbpsor10Gbps.Confirm that communication speed for each port is the same value. Note that setting a different speed for each port is not allowed.
-
Click Next.
-
Configure the IPv4 network settings as required and click Next.
-
Configure the IPv6 network settings as required and click Finish.
-
-
In the iSCSI switch settings, fix the port speed (25Gbps or 10Gbps) and disable the Forward Error Correction (FEC) mode. The procedure to disable the FEC mode varies depending on the switch.
Refer to the manuals for the switches to be used.
Notes Related to the Configuration of IP Addresses
SANtricity 11.60.2 and later
If an arbitrary IP address is assigned to the iSCSI network settings or the management port for the storage system network, an error message is output to SANtricity System Manager and the IP address may not be set.
"The operation cannot complete because of an incorrect parameter in the command sent to the controller. Please retry the operation. If this message persists, contact your Technical Support Representitive. (API 4)"
SANtricity OS has reserved IP addresses for internal operations. These addresses cannot be assigned as arbitrary IP addresses for the storage system, such as for the iSCSI and management ports.
The following IP addresses cannot be assigned.
-
SANtricity 11.60.2 to 11.70.5
-
IPv4 address
192.0.0.0/17 (192.0.0.0 to 192.0.127.255)
-
IPv6 address
fd94:29f8:cf58::/48
-
-
SANtricity 11.80 and Later
-
IPv4 address
192.0.0.0/22 (192.0.0.1 to 192.0.3.255)
-
IPv6 address
fd94:29f8:cf58:1::2/48
-
Assign an IP address other than the IP addresses that cannot be assigned.
Storage System Configuration Change for the Administrator Due to HBA Replacement
For an HBA replacement due to an HBA configuration change or HBA failure, addition or deletion work of the WWN (hereinafter referred to as the "host port") in SANtricity System Manager is required.
In addition, when configuring Fabric, changing of the zone setting in the switch may be required.
Whether or not the configuration change is required depends on the zone setting method.
Before performing the work, check the following information.
-
The hostname of the change target HBA
-
The WWN assigned to the host port of the change target HBA
-
The label attached to the host port of the change target HBA
-
The WWN of the new HBA
Perform the HBA replacement according to the HBA replacement procedure of the server.
Make sure to refer to the server manual to perform the replacement work.
After the HBA replacement, perform the setting changes in the host settings.
-
Delete the host port to be replaced on the target host.
-
Add a new HBA host port to the target host.
If zoning is set on the server and storage system, when a host port is being added, the new HBA host port that is displayed can be selected.
Make sure the disks are recognized by the OS in the same way as before the replacement.
-
For RHEL
Check the disks with
multipath -ll. -
For VMware
Check the device from the storage adapter of vCenter.
-
For Windows
Check the disks from Disk Management.
Notes When a Marvel (Qlogic) Made FC HBA Is Used
In a SAN Boot configuration, if the access path to the LUN where the OS is installed is only on the controller side that is not displayed in [Current Owner], the OS may fail to boot.
-
Example of a system state where this phenomenon has occurred
If the controller (Ctrl) that owns OS LUN#0 is A, the access path between HBA 0 and Ctrl A is disconnected for some reason.
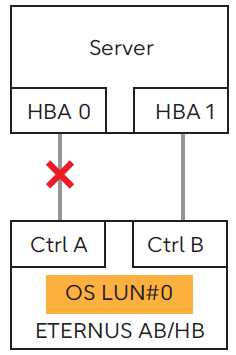
The SAN Boot configuration when the PY-FC432/431, PY-FC412/411, PY-FC342/341, or PY-FC322/321 is used.
Because the LUN in the path on the controller side that is not displayed in Current Owner is not recognized by the UEFI of PRIMERGY, PRIMERGY cannot access the LUN in the path on the controller side that is not displayed in Current Owner.
However, because the OS recognizes the LUN from Current Owner and non Current Owner controller paths, once the OS is started, a redundant configuration can be created without any problems.
When booting the server, make sure the access path of the LUN where the OS is installed is connected to a controller displayed in Current Owner.
Current Owner can be changed from SANtricity System Manager of the ETERNUS AB/HB series.
-
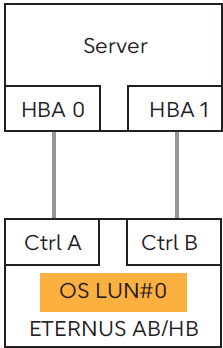
System state where this phenomenon does not occur Both access paths are normal
-
If the controller (Ctrl) that owns OS LUN#0 is A, the path between HBA 0 and Ctrl A is normal
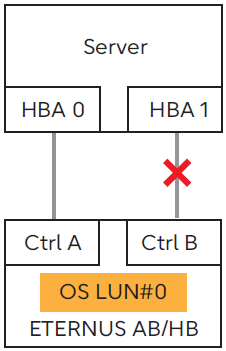
In a multipath configuration that includes both controllers, if the path on the controller side (or the Current Owner for the OS LUN) is disconnected, this phenomenon occurs because only the path on the non Current Owner side has access to the LUN.
Therefore, this event will not occur during startup, or when the system, such as the path, is normal.
Impact to the system after startup has not been confirmed.
